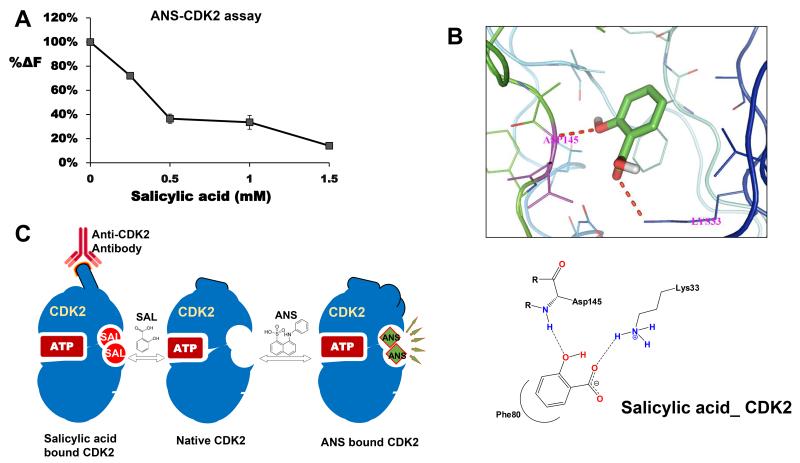
Figure 6.
A, effect of pre-incubation of salicylic acid with CDK2 on fluorescence due to ANS. CDK2 (1.6 μM) was incubated with ANS (50 μM) alone or with salicylic acid at different concentrations, fluorescence measured as described in the text. Salicylic acid mediated decrease in fluorescence was compared with fluorescence due to ANS/CDK2. The decrease in fluorescence was expressed as a percentage of control; B, is the molecular docking studies showing interactions of salicylic acid with CDK2; C, a model showing potential salicylic acid binding to CDK2. We predict that salicylic acid binds to an allosteric site on CDK2, similar to a site described for ANS binding to CDK2. Binding of salicylic acid to CDK2 changes the conformation; increases the ability of anti-CDK2 antibody to immunoprecipitate CDK2 due to a better exposure of the epitope. Binding of salicylic acid to CDK2 would also quench the fluorescence due to ANS. We predict that potential allosteric inhibitors could be developed by screening new salicylic acid derivatives with allosteric binding potential and inhibition of CDK2 activity.