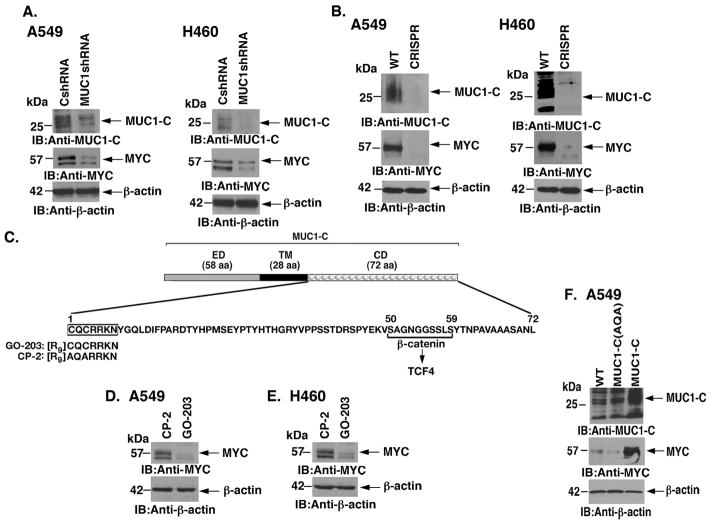
Figure 1. Targeting MUC1-C downregulates MYC expression.
A. A549 (left) and H460 (right) lung cancer cells were transduced with lentiviral vectors to stably express a Control shRNA (CshRNA) or a MUC1 shRNA. Lysates from the indicated cells were immunoblotted with antibodies against MUC1-C, MYC and β-actin as a control. B. A549 (left) and H460 (right) cells were silenced for MUC1 using CRISPR/cas9. Lysates from wild-type (WT) and CRISPR cells were immunoblotted with the indicated antibodies. C. Schema of the MUC1-C subunit with a 58 amino acid (aa) extracellular domain (ED) and the 28 aa transmembrane domain (TM). The sequence of the 72 aa cytoplasmic domain (CD) is highlighted at the CQCRRKN motif, which is targeted by the cell penetrating GO-203 peptide and not the control CP-2 peptide. Also highlighted is the β-catenin binding site (SAGNGGSSLS). D and E. A549 (D) and H460 (E) cells were treated with 5 μM GO-203 or CP-2 for 48 h. Lysates were immunoblotted with the indicated antibodies. F. A549 cells were transduced to stably express MUC1-C or MUC1-C(AQA). Lysates from the indicated cells were immunoblotted with antibodies against MUC1-C, MYC and β-actin.