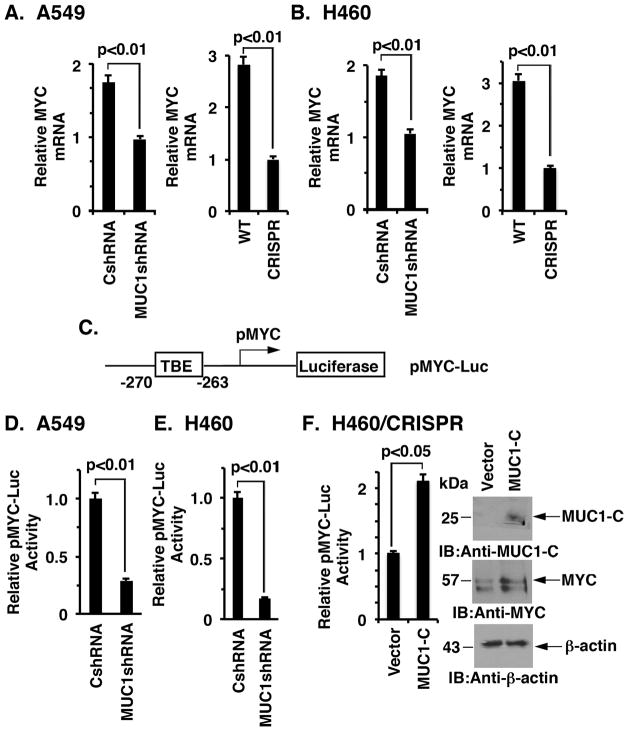
Figure 2. Targeting MUC1-C suppresses MYC transcription.
A and B. The indicated A549 (A) and H460 (B) cells were analyzed for MYC mRNA levels by qRT-PCR. The results (mean±SD of three determinations) are expressed as relative MYC mRNA levels as compared to that obtained for the MUC1-C silenced cells (assigned a value of 1). C. Schema of the Del4 pMYC-Luc reporter with positioning of the TCF4 binding element (TBE) at position −270 to −263 upstream to the transcription start site. D and E. The indicated A549 (D) and H460 (E) cells were transfected with the pMYC-Luc reporter for 48 h and then assayed for luciferase activity. The results are expressed as the relative luciferase activity (mean±SD of three determinations) compared with that obtained the cells expressing the control CshRNA (assigned a value of 1). F. H460/CRISPR cells were transiently transfected to express an empty vector or one expressing MUC1-C and the pMYC-Luc reporter for 48 h. The results are expressed as the relative luciferase activity (mean±SD of three determinations) compared with that obtained the cells expressing the control vector (assigned a value of 1)(left). Lysates from the indicated cells were immunoblotted with antibodies against MUC1-C, MYC and β-actin (right).