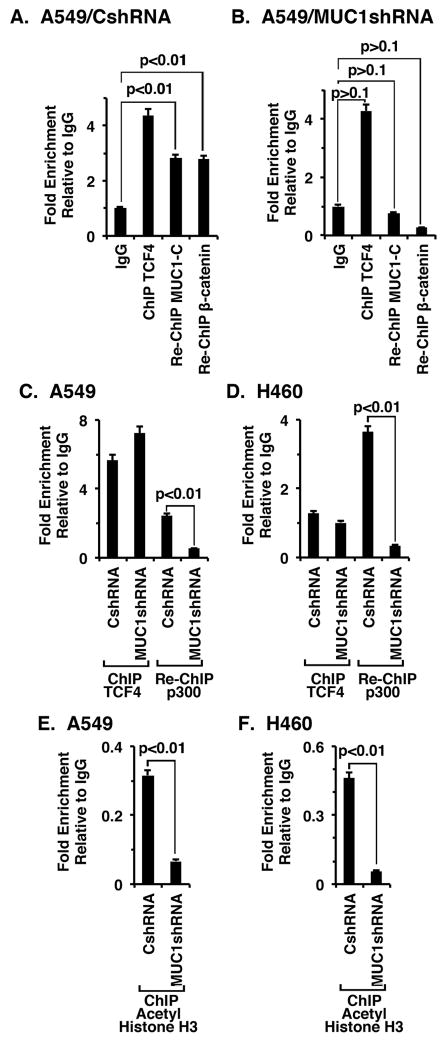
Figure 4. MUC1-C occupies the MYC promoter with TCF4 and β-catenin and regulates histone H3 acetylation.
A and B. Soluble chromatin from the indicated A549/CshRNA (A), A549/MUC1shRNA (B) cells was precipitated with anti-TCF4 or a control IgG. In the re-ChIP experiments, TCF4 precipitates were released and reimmunoprecipitated with anti-MUC1-C or anti-β-catenin. The final DNA samples were amplified by qPCR with primers for the MYC promoter TBE binding region or as a control GAPDH. The results (mean±SD of three determinations) are expressed as the relative fold enrichment compared with that obtained with the IgG control. C and D. Soluble chromatin from the indicated A549 (C) and H460 (D) cells was precipitated with anti-TCF4 or a control IgG. In the re-ChIP experiments, TCF4 precipitates were released, reimmunoprecipitated with anti-p300 and then analyzed for MYC promoter sequences by qPCR. The results (mean±SD of three determinations) are expressed as the relative fold enrichment compared with that obtained with the IgG control. E and F. Soluble chromatin from the indicated A549 (E) and H460 (F) cells was precipitated with anti-acetylated histone H3 or a control IgG, and then analyzed for MYC promoter sequences by qPCR. The results (mean±SD of three determinations) are expressed as the relative fold enrichment compared with that obtained with the IgG control.