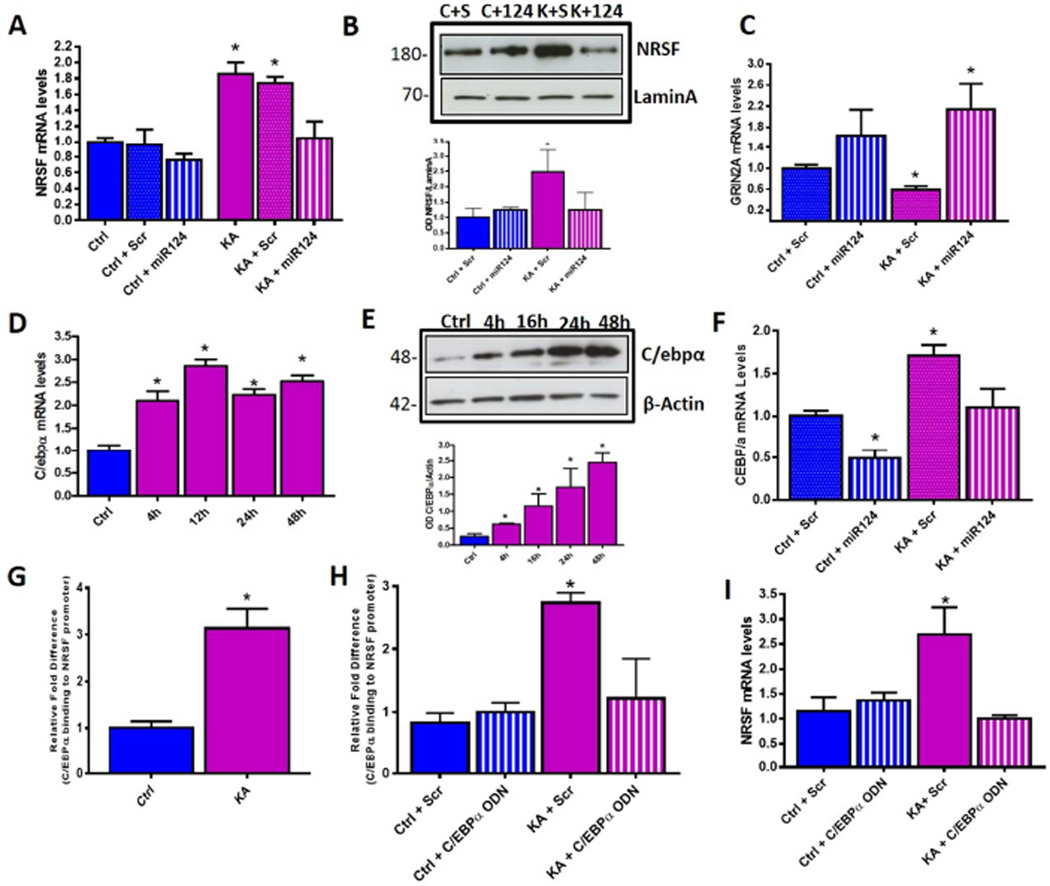
Figure 4. MiR-124 repression is required for increased NRSF expression and this regulation is mediated by miR-124 target C/EBPα.
(A) Hippocampal NRSF mRNA levels in controls vs KA-SE rats given either miR-124 agomir or Scr infusion. Hippocampal NRSF mRNA levels increased 48h following KA-SE+Scr and this increase was blocked in rats given miR-124 agomirs immediately following SE (KA+miR-124); n=6/group. (B) NRSF protein levels in nuclear fraction of hippocampus extracts in control and KA animals receiving either Scr or miR-124 infusion. NRSF protein levels were higher in SE+Scr hippocampus 48h following insult compared to SE+miR-124, where levels were comparable to controls. n=6/group, 1 hippocampus/lane. (C) MiR-124 agomir, but not Scr, treatment prevented seizure-induced NRSF-mediated repression of GRIN2A; n=6/group. (D) Hippocampal C/EBPα mRNA levels were enhanced significantly 4h following KA-SE and remained elevated up to 48h, n=8/time-point; qPCR. (E) C/EBPα protein levels increased 4h post SE and remain elevated for at least 48h. Representative W. blot and quantification. n=5/group. (F) MiR-124 agomir treatment following KA-SE prevented seizure-induced increase of C/EBPα expression compared to KA-SE which received Scr agomirs; n=6/group. (G) C/EBPα occupancy at NRSF gene increased significantly following KA-SE as compared to controls, n = 6/group. See Figure S4 for examined binding sites using ChIP-qPCR. (H) C/EBPα binding to the NRSF gene after KA-seizures was attenuated in hippocampi treated with ordered ODNs, compared to Scr ODN, n=3/group. (I) Inhibition of C/EBPα binding prevented seizure-induced NRSF upregulation. n=3/group.