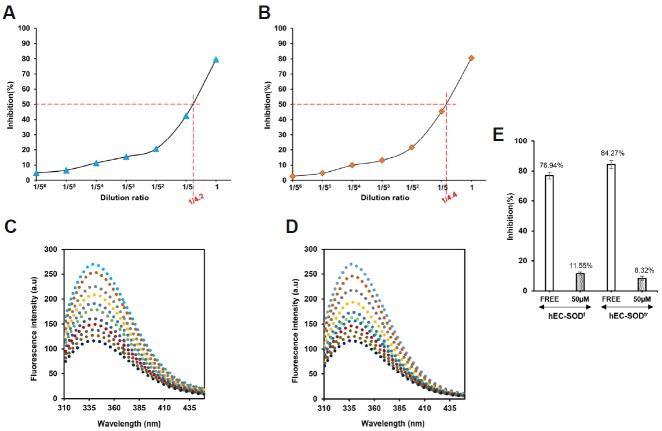
Fig. 3.
Enzyme activity and binding affinity of an inhibitor (DDC) of hEC-SODf and hEC-SODtr in the presence of 0.1% BSA & 50 μM Cu/Zn. (A) Activity assay of hEC-SODf in the presence of 0.1% BSA, and 50 μM Cu/Zn ions. (B) Activity assay of hEC-SODtr in the presence of 0.1% BSA, and 50 μM Cu/Zn ions. (C) Fluorescence assay of hEC-SODf with inhibitor (Na-DDC) in the presence of 0.1% BSA; 50 μM Cu/Zn. (D) Fluorescence assay of hEC-SODtr with inhibitor (Na-DDC) in the presence of 0.1% BSA; 50 μM Zn/Cu. Protein samples were excited at 280 nm and emission spectra were recorded from 300 to 450 nm. All the assays were performed in phosphate-buffered saline (PBS; pH 7.4) using 20 μM hEC-SOD with an increasing concentration of inhibitor (Na-DDC). [
 0 μM;
0 μM;
 10 μM;
10 μM;
 20 μM;
20 μM;
 30 μM;
30 μM;
 40 μM;
40 μM;
 50 μM;
50 μM;
 60 μM;
60 μM;
 70 μM;
70 μM;
 80 μM;
80 μM;
 90 μM and
90 μM and
 100 μM]. (E) Effect of Na-DDC (inhibitor) on hEC-SOD activity. Enzyme activity of hEC-SOD was determined using the SOD Assay Kit WST-1 (Dojindo Laboratories) in PBS buffer (pH 7.4) in the absence and presence of 50 μM of inhibitor (Na-DDC).
100 μM]. (E) Effect of Na-DDC (inhibitor) on hEC-SOD activity. Enzyme activity of hEC-SOD was determined using the SOD Assay Kit WST-1 (Dojindo Laboratories) in PBS buffer (pH 7.4) in the absence and presence of 50 μM of inhibitor (Na-DDC).