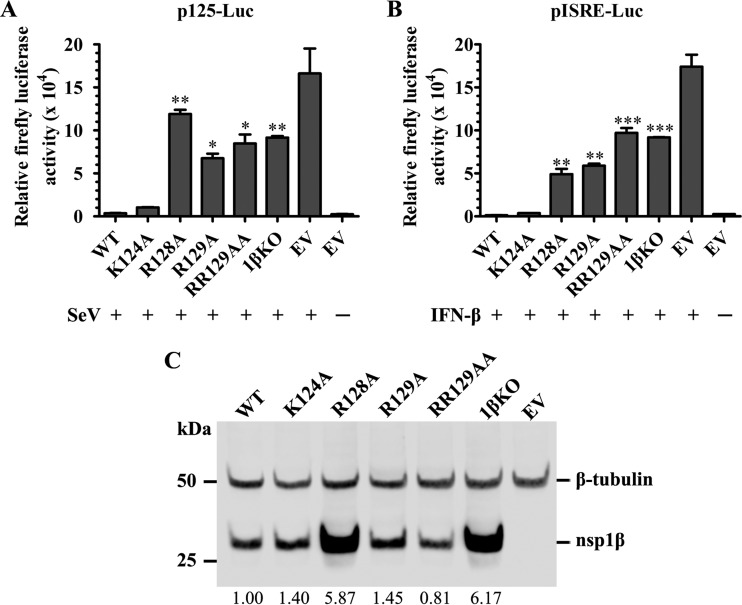
FIG 1.
Mutations in the GKYLQRRLQ motif impair nsp1β's inhibitory effect on type I interferon production and signaling. (A and B) HEK-293T cells in a 24-well plate were cotransfected with a plasmid expressing WT nsp1β or the nsp1β mutant, the p125-Luc reporter plasmid expressing firefly luciferase under the control of the IFN-β promoter (A) or pISRE-Luc expressing firefly luciferase derived from the interferon-stimulated response element (ISRE) (B). An empty vector (EV) was used as a control. At 24 h posttransfection, cells were stimulated with SeV at 100 HA units/ml or stimulated with IFN-β at 2,000 IU/ml for 16 h. Cell lysates were harvested for measurement of luciferase activity. (C) The expression level of nsp1β was evaluated by Western blot analysis using nsp1β-specific MAb 123-128. β-Tubulin was detected as a loading control. The membrane was incubated with a mixture of primary anti-FLAG M2 MAb (Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO) and MAb against β-tubulin. The secondary antibody IRDye 800CW goat anti-mouse IgG(H+L) (Li-Cor Biosciences, Lincoln, NE) was used for visualizing the target proteins with a digital image system (Odyssey infrared imaging system; Li-Cor Biosciences, Lincoln, NE). The expression of nsp1β was quantified and normalized to the expression level of β-tubulin, and the relative expression levels are shown under each band. Statistical significance between the wild-type virus-infected group and the mutant virus-infected group was determined by one-way ANOVA and Tukey's test and is indicated with asterisks (*, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001).