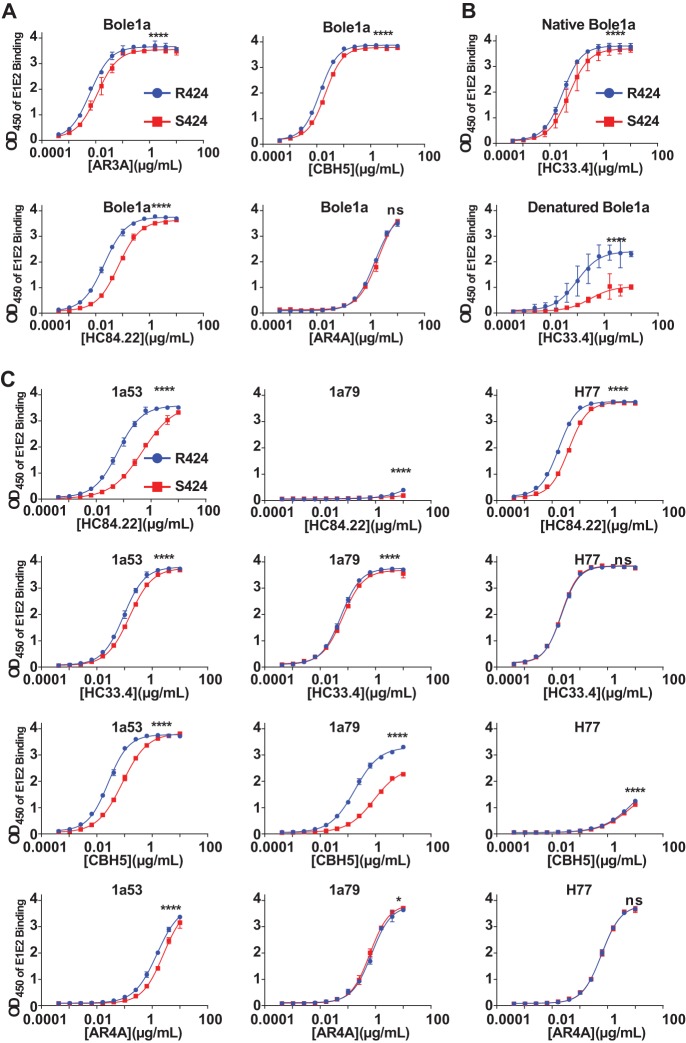
FIG 6.
Mutation of arginine 424 to serine confers resistance to binding of broadly neutralizing monoclonal antibodies. (A) Binding of MAbs AR3A, CBH-5, HC84.22, and AR4A to Bole1a_R424 and Bole1a_S424 E1E2 lysates was measured by ELISA. MAbs were assayed in duplicate with 2.5-fold serial dilutions, starting at 10 μg/ml, and binding was detected using HRP-conjugated anti-human IgG secondary antibody. Values shown represent the means of the results determined with two replicates, and error bars indicate standard deviations. P values were determined by two-way ANOVA (****, P < 0.0001). (B) To compare the binding results seen under native and denatured E1E2 conditions, Bole1a_R424 and Bole1a_S424 E1E2 lysates were diluted either in a denaturing buffer containing sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) or in phosphate-buffered saline (PBS). The denatured lysates were also boiled for 5 min and then cooled on ice. Both native and denatured lysates were then added to G. nivalis lectin-coated plates, and binding of serial dilutions of MAb HC33.4 was quantitated in duplicate. Data shown represent the means of the results of two independent experiments, and error bars indicate standard deviations. (C) Binding of MAbs HC84.22, HC33.4, CBH-5, and AR4A to 1a53, 1a53_S424, 1a79, 1a79_S424, H77, and H77_R424 E1E2 lysates was measured by ELISA as described in the panel A legend. P values were determined by two-way ANOVA (*, P < 0.05; ****, P < 0.0001).