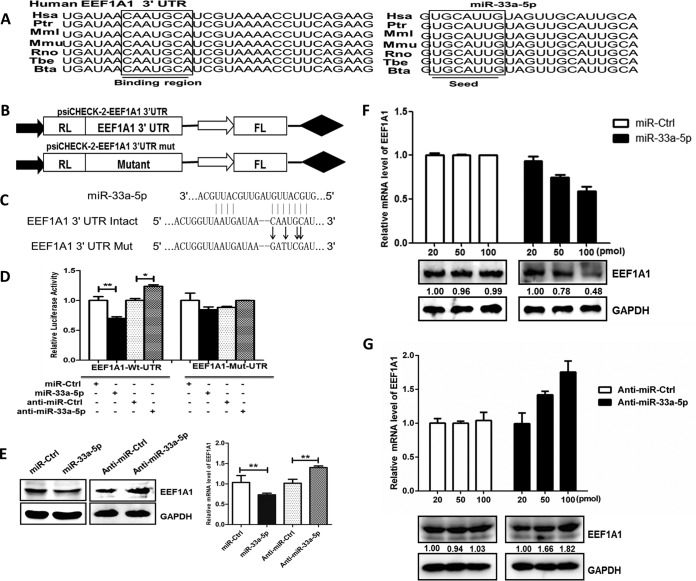
FIG 3.
EEF1A1 is a target of miR-33a-5p. (A) Sequence alignments of miR-33a-5p in different species and its target sites in 3′ UTR of EEF1A1. (B) Model of wild and mutant constructs of EEF1A1 3′ UTR. (C) Schematic representation of mutant reporters of EEF1A1 3′ UTR. The frame and bold letters indicate the point mutation. (D, E, and F) EEF1A1 3′ UTR is a target for miR-33a-5p. (D) Wild or mutant reporter constructs of EEF1A1 3′ UTR were cotransfected with indicated oligonucleotides into HEK293T cells. After 24 h, the Renilla and firefly luciferase activities were assayed. (E) HEK293T cells were transfected with miR-33a-5p mimics or miR-33a-5p inhibitor for 48 h, and the EEF1A1 mRNA and protein expression levels were determined by quantitative real-time PCR (normalized to β-actin) and Western blotting (normalized to GAPDH), respectively. (F and G) HEK293T cells were transfected with different concentrations of miR-33a-5p mimics (F) or miR-33a-5p inhibitors (G) for 24 h and then infected with JEV at an MOI of 1.0. At 48 h postinfection, the EEF1A1 protein levels were determined by Western blotting and normalized to GAPDH. EEF1A1 mRNA levels were determined by quantitative real-time PCR and normalized to β-actin. Data are shown as means ± SEM of at least three independent experiments. *, P < 0.05; ***, P < 0.001.