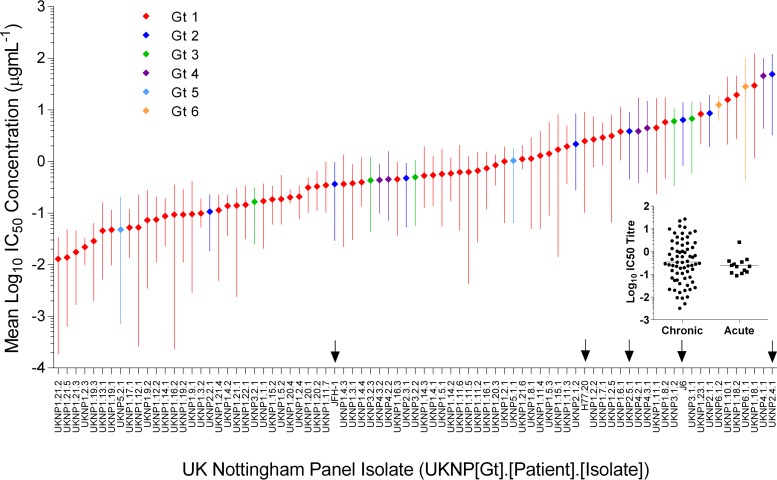
FIG 4.
Pseudotype viruses incorporating different E1E2 clones derived from the major HCV genotypes display diverse susceptibilities to antibody neutralization. Eighty-one distinct patient-derived and reference E1E2 clones were assessed for neutralization sensitivities using five monoclonal antibodies. The mean log10 IC50 neutralization value, and the range, for each HCVpp supplemented with E1E2 derived from genotypes 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, and 6 were plotted in rank order from lowest (most sensitive) to highest (least sensitive). The arrows indicate the clones that were used in the subsequent HCVcc analysis. The inset graph shows the mean neutralization IC50s for E1E2 genes sampled from either acute or chronic HCV infection. Both groups possessed similar neutralization resistance phenotypes, as shown by a one-way analysis of variance.