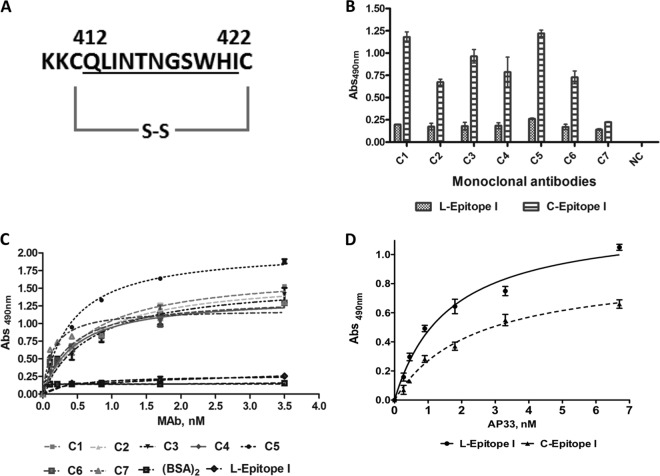
FIG 1.
Selection of MAbs specifically binding to the cyclic variant of epitope I. (A) Primary structure of the C-epitope I peptide representing the HCV E2 region from residues 412 to 422. The peptide was C-terminally amidated, N-terminally acetylated, and cyclized using two cysteines introduced at either end of the native sequence (underlined). (B) ELISA screening of hybridoma supernatants. C-epitope I and L-epitope I were coated onto microtiter plates at 0.5 μg/ml. Hybridoma supernatants were added, and bound antibodies were detected with an HRP-conjugated anti-mouse immunoglobulin antibody. Trastuzumab was used as a negative control (NC) and was used at the same concentration as the test MAbs. (C) Dose-dependent binding of purified MAbs C1 to C7 to C-epitope I. The MAbs did not bind to L-epitope I or BSA2 (glutaraldehyde-self-conjugated BSA); only the negative binding data for MAb C2 are shown. (D) Binding of MAb AP33 to L- and C-epitope I peptides. Abs, absorbance.