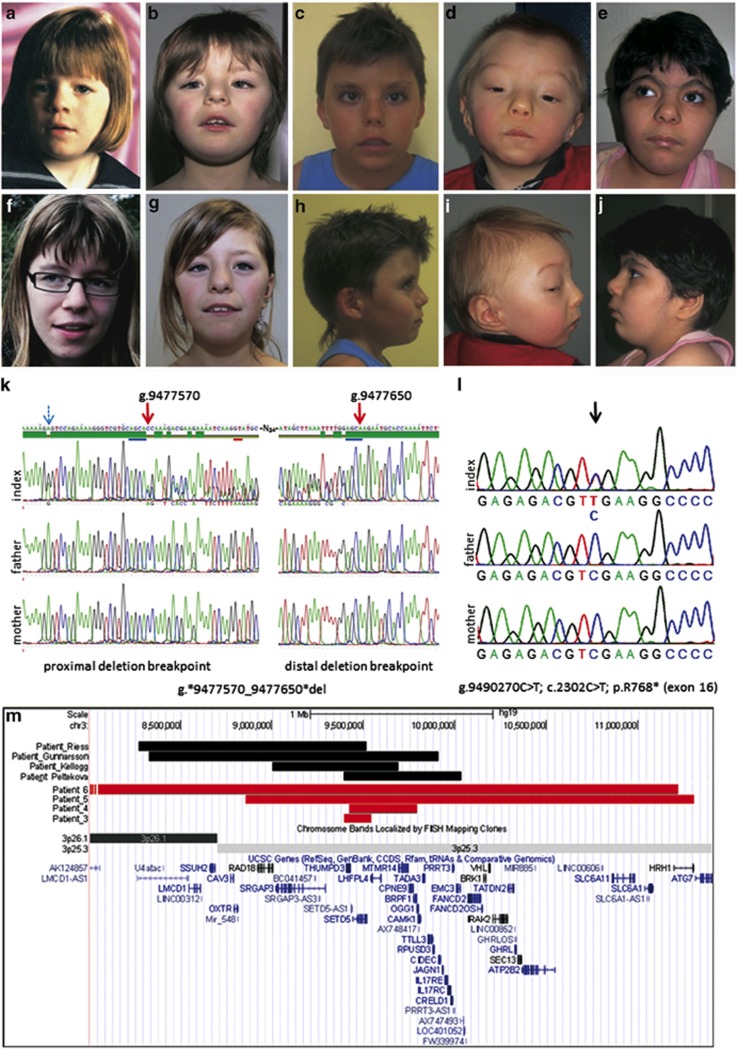
Figure 1.
Facial phenotypes of individuals with a SETD5 sequence variant or microdeletion, results of the mutation analysis and the size and localisation of overlapping deletions. (a–j) Facial phenotypes of patients 1–5 (consent for the publication of photographs of patient 6 was withdrawn). All six patients share certain facial phenotypic features, in particular a broad nasal bridge, anteverted nares, a long philtrum and downturned corners of the mouth. (a, f) show patient 1 who carries an 81 bp deletion (Figure 1k) at different ages; (b, g) show patient 2 who carries a nonsense variant (Figure 1l) ) at different ages; (c, h) patient 3; (d, i) patient 4 and (e, j) patient 5. (k, l) electropherograms of the variant verifications by Sanger sequencing in patients. (k) Scheme of the 81 bp de novo deletion identified in patient 1. The first and last nucleotides of the deletion are marked with red arrows, and the last four nucleotides before the deletion (AGCA) and the last four nucleotides of the deleted segment (also AGCA) are underlined in blue. The splice-donor site (GT) of intron 7 is underlined by a red bar. An additional de novo base substitution (A>G leading to AGT>GGT, Ser>Gly) is indicated by a blue dashed arrow (details: Supplementary Figure 1). (l) de novo nonsense base substitution found in patient 2. (m) Scheme of overlapping deletions of patients 3–6 compared with those previously published in the literature.