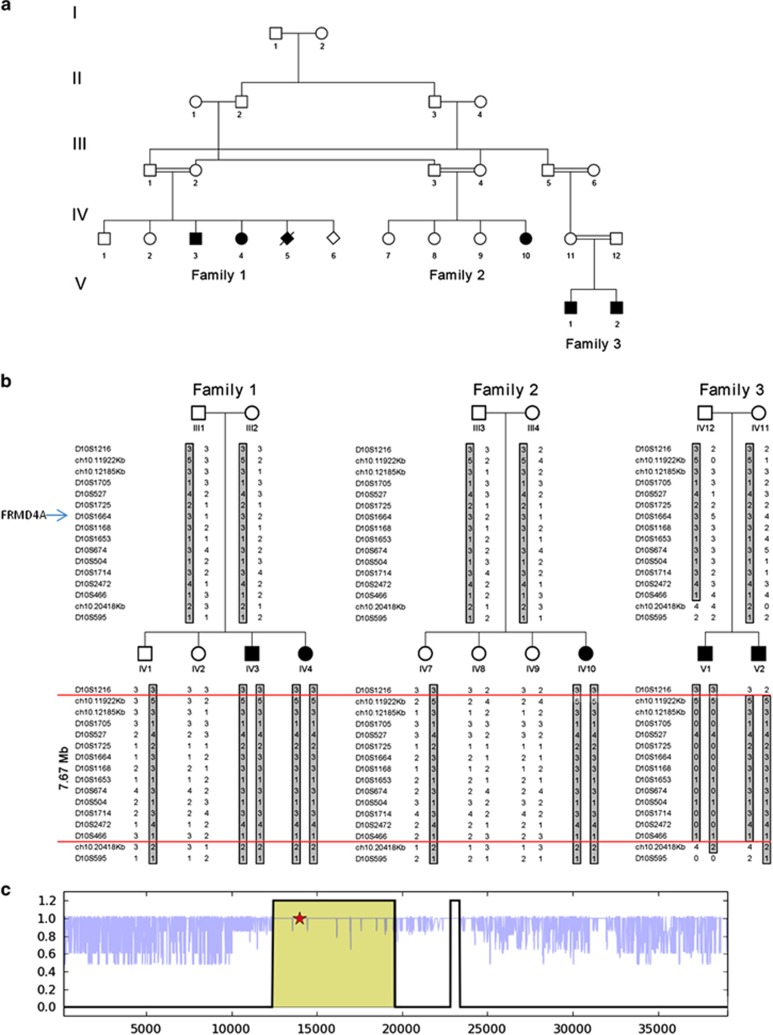
Figure 1.
The affected kindred and fine mapping of the chromosome 10p locus: (a) Family tree of the affected kindred. (b) Fine mapping of the disease-associated locus. Haplotype of the locus in linkage with the disease. The disease-associated haplotype is boxed, and the minimum homozygous haplotype shared by all the affected individuals and by their obligatory carriers is defined by the red lines, markers ch10.11922Kb and D10S466. (c) Location of the mutated gene within the disease-associated locus (output of the homozygosity mapping tool for part of chromosome 10). The analysis shows the level of allele sharing between all affected individuals in gray lines (between 0 and 1). Confirmed shared blocks for all affected individuals are indicated by the thick black line. Within the regions, a few single-nucleotide polymorphisms are not homozygous due to background noise which reflects the error rates in the data. The highlighted region shows the disease-associated locus and the red star marks the location of the mutated gene, FRMD4A. The full colour version of this figure is available at European Journal of Human Genetics online.