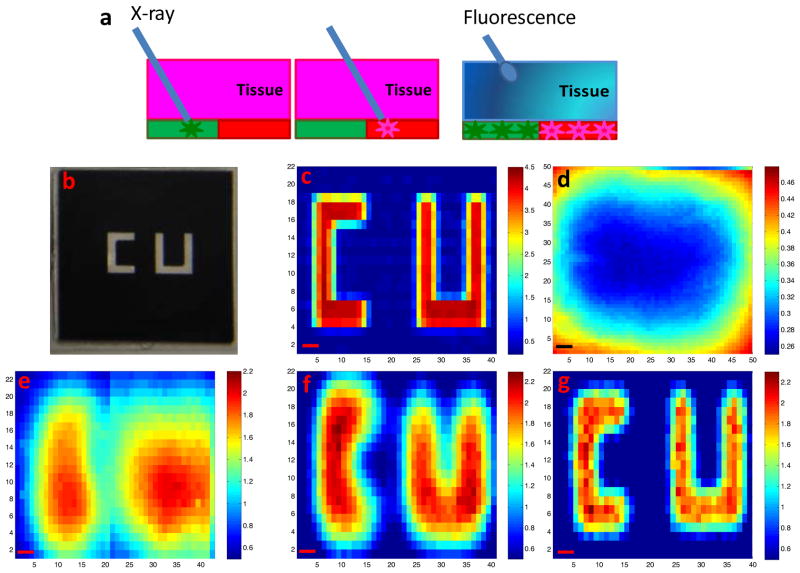
Figure 3.
Spatial resolution of XELCI. (a) Working principle of XELCI versus fluorescence tomography. (b) Photograph of “CU” (target) on transparency. (c) Target mapping without tissue, irradiated with 1.5 mm X-ray beam. (d) Target mapped through tissue with white light as the illumination source. (e) Target mapped through tissue, irradiated with 3 mm X-ray beam. (f) Target mapped through tissue, irradiated with 1.5 mm X-ray beam; (g) Target mapped through tissue, irradiated with 1 mm X-ray beam. The color bars on the right are the ratios of the peak intensity at 620 nm over that at 700 nm. The x and y axis in c-g represent position. Step size=300 μm, scale bar= 1 mm.