Fig. 1.
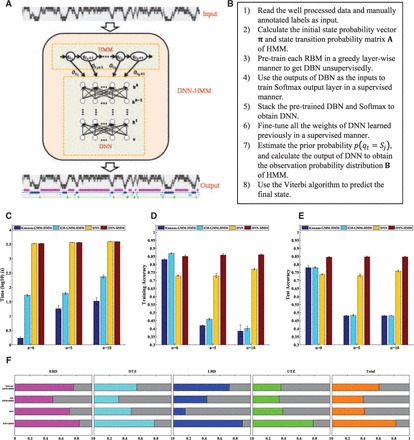
Development and performance assessment of the DNN–HMM algorithm. (A) Diagram of the DNN–HMM algorithm. In the DNN–HMM hybrid architecture, the HMM models the sequential property of the replication timing signal obtained from Repli-Seq data, and the DNN models the scaled observation likelihood probability distribution. (B) Pseudocode of the main steps to train the DNN–HMM. (C–E) Performance comparisons in terms of the computation time (C), training accuracy (D) and test accuracy (E) between the DNN–HMM algorithm and the three additional algorithms that we have implemented. ‘n = 0’ means that we use the original six-dimensional Repli-Seq data as inputs, ‘n = 5’ means that we concatenate five neighbours on both sides of the original, and ‘n = 10’ means that we concatenate 10 neighbours on both sides of the original. (F) Proportion of the replication domains of each type that are reproduced from another independent biological replicate of the Repli-Seq data in BJ cells by employing four algorithms
