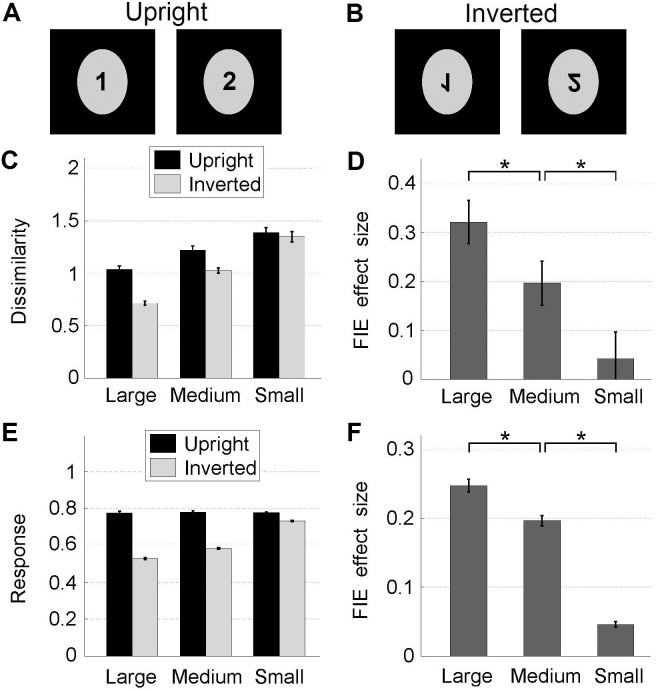
Fig 2. Tuning size accounts for the Face Inversion Effect (FIE) at the behavioral and neural levels.
(A-B) Schematic for the FIE: dissimilarity between faces is more apparent for upright (A) than inverted (B) faces. (C) Mean dissimilarities between patterns of C2 responses to two different faces, for all possible pairs of faces. (D) Behavioral FIE effect size (upright dissimilarity–inverted dissimilarity in (C)) varies with tuning size. (E) Results for the neural-level FIE, i.e. mean individual C2 model neuron responses to each face (as opposed to dissimilarities between sets of neural responses to pairs of faces, in (C)) for upright vs. inverted faces. (F) Neural-level FIE effect size (upright response–inverted response in (E)) varies with tuning size. Error bars: SEM.