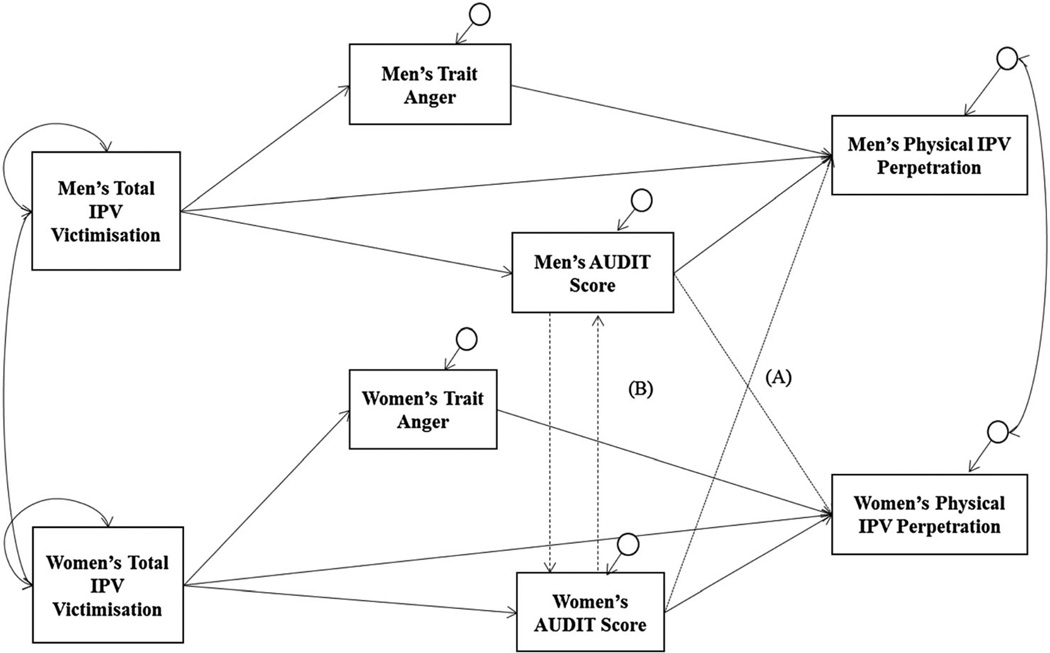
Figure 1.
Hypothesised models. For Model 1, anger and problematic alcohol use partially mediate the association between IPV victimisation and IPV perpetration (solid lines), with (A) partner problematic alcohol use as direct effect on actor IPV perpetration (dotted lines). Model 2 tests the same partial mediating pathways for anger and alcohol use, but presents (B) a feedback loop for partner drinking on actor drinking (dashed lines) instead of direct effects on partner IPV perpetration. Model 3 removes all partner influences and tests a parsimonious model for comparison (solid lines only)