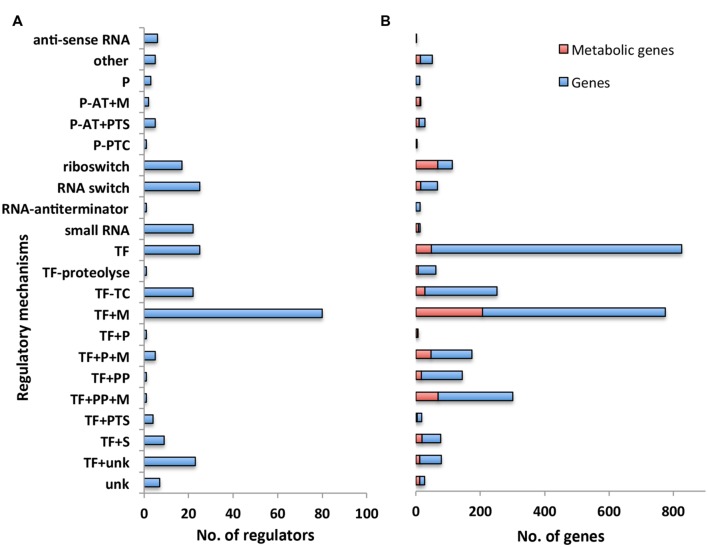
FIGURE 2.
Overview of regulatory network categorized by regulatory mechanism. (A) Number of regulators with respect to their regulatory mechanisms. Each bar corresponds to the number of regulators having the same type of regulatory mechanism. (B) Number of genes with respect to the regulatory mechanisms controlling their expression. Each bar refers to the number of genes that are controlled by a regulator having the same type of regulatory mechanism. Number of genes involved in the metabolism is highlighted in red. Abbreviations: P (Accessory protein involved in regulation); P-AT+M (Protein – transcriptional antiterminator conditioned by a metabolite); P-AT+PTS (Protein – transcriptional antiterminator conditioned by a PTS phosphorylation); P-PTC (Protein post-transcriptional control); TF (Transcription factor); TF–TC (Two-component response regulator); TF+M (Transcription factor conditioned by a metabolite); TF+P (Transcription factor + accessory protein); TF+P+M (Transcription factor + accessory protein associated to a metabolite); TF+PP (Transcription Factor + phosphorylated protein); TF+PP+M (Transcription factor + phosphorylated protein + metabolite); TF+PTS (Transcription factor + PTS phosphorylation); TF+S [Transcription factor + stress (DNA alteration/TF alteration)]; TF+unk (Transcription factor conditioned by an unknown mechanism/protein/metabolite).