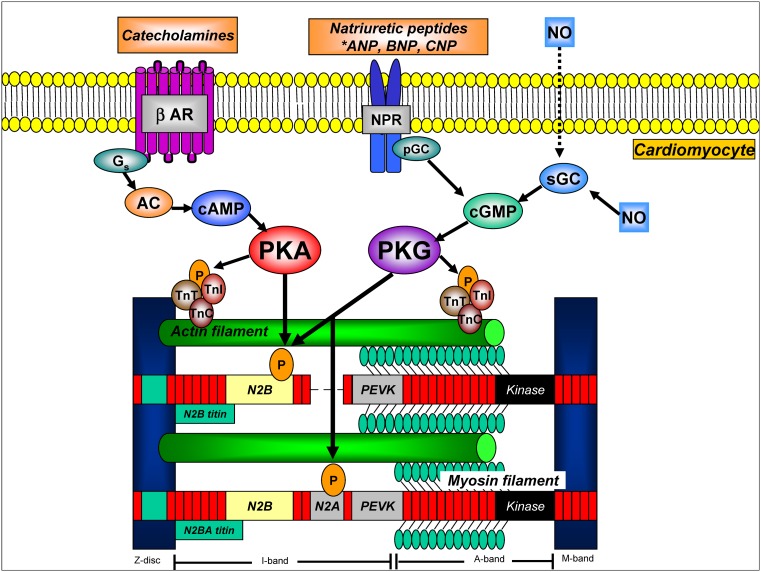
Fig. 1.
Cardiomyocyte cAMP and cGMP signalling pathways involved in myofilament regulation and titin-based stiffness. Stimulation of β-ARs activates Gs -AC-mediated generation of cAMP, which stimulates PKA activity. cGMP is generated from activation of sGC by NO and from activation of pGC by NPs. cGMP stimulates PKG activity. Both PKA and PKG induce lusitropic effects through phosphorylation of TnI, and lower cardiomyocyte stiffness through phosphorylation of the titin N2B segment. Circled P’s indicate phosphorylatable sites. AC adenylyl cyclase, βAR beta-adrenergic receptor, cAMP cyclic adenosine monophosphate, G G-stimulatory protein, NPR natriuretic peptide receptor, PEVK unique sequence rich in proline, glutamic acid, valine and lysine