Fig. 13.
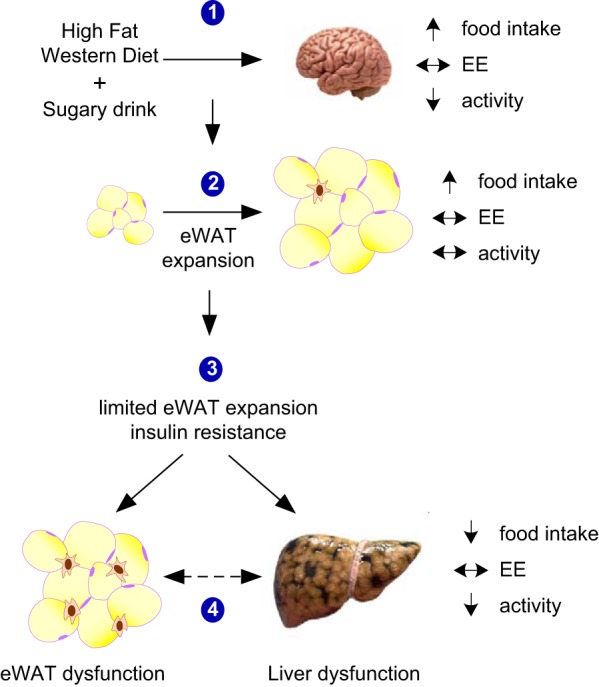
Model of the metabolic and pathophysiological effect of consuming a HFWD + sugary drinking water in mice. Events are 1) acute hyperphagic response to consumption of the diet in the absence of changes to energy expenditure is observed at 24 h and after 2 wk on the diet; 2) rapid eWAT expansion; 3) inability of eWAT to further expand, coupled with liver and adipose insulin resistance; and 4) adipose and liver dysfunction characterized by inflammation and progression to nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), respectively. The interaction between dysfunctional adipose tissue and the liver is still not fully known (dashed line).
