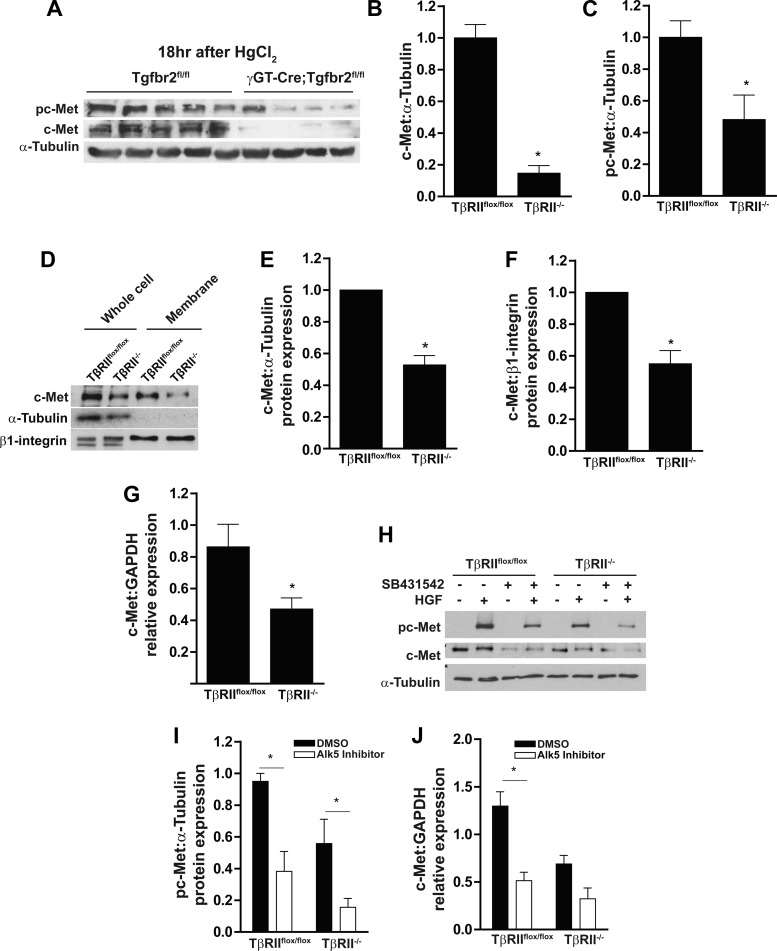
Fig. 2.
PTs lacking TβRII in vitro have reduced c-Met membrane localization and transcript levels. A–C: cortical tissue lysates of γGT-Cre;Tgfbr2flox/flox (conditional deletion of TβRII in the PT) and Tgfbr2flox/flox (floxed control) mice were subjected to HgCl2-induced acute kidney injury and immunoblotted for c-Met expression and phosphorylation with α-tubulin as a loading control, and protein expression was quantified. D: lysates of whole cell and membrane preparations (see methods) were immunoblotted for c-Met expression with α-tubulin, which was used to show the purity of membrane preparations, and β1-integrin, which was used as a loading control for membrane expression. E and F: quantification of c-Met expression in whole cell lysates and membrane preparations, with PT cell expression of TβRIIflox/flox in each experiment (n = 3) adjusted to 1. G: qPCR analysis of c-Met mRNA in TβRIIflox/flox and TβRII−/− PT cells normalized to GAPDH expression (n = 3). H and I: PT cells pretreated for 4 days with an ALK5 inhibitor (SB431542) or vehicle control (DMSO) were stimulated with HGF and immunoblotted for c-Met phosphorylation, and protein expression was quantified using α-tubulin as loading control (n = 3). J: PT cells were pretreated for 4 days with an ALK5 inhibitor (SB431542) or vehicle control (DMSO), RNA was isolated and converted to cDNA, and c-Met transcription was quantified by qPCR. Values are means ± SE. *P < 0.05.