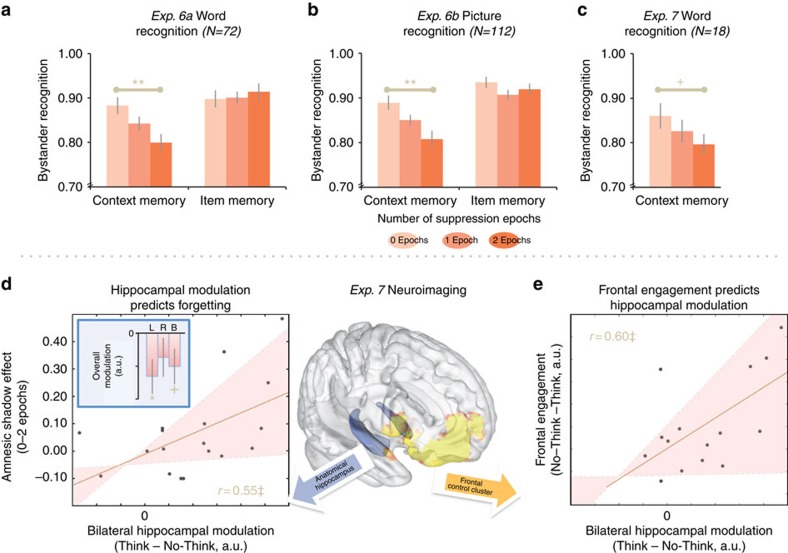
Figure 4. Amnesic shadow in recognition.
(a) Memory for context, not items, is impaired for words (F-test). (b) Replication with pictures. (c) Context amnesia in experiment 7. (d) Right-most inset bar illustrates mean (error bar, s.e.m.) bilateral hippocampal modulation (blue anatomical region of interest seen in adjoining glass brain) during suppression, relative to retrieval in arbitrary units (a.u.). Modulation (two-tailed t-tests) in left and right hippocampi also is plotted separately for exploratory purposes (with Bonferroni correction for multiple corrections across the two hemispheres). Across participants, modulation predicted context amnesia (outlier-skipped Pearson bootstrap 95% confidence interval (CI): (0.13, 0.79)). Q (e) Suppression-related frontal engagement (yellow No-Think>Think functional mask) predicted hippocampal modulation (bootstrap CI: (0.03, 0.87)). Robust correlation removed bivariate outliers from relevant analysis/plot. Error bars for behaviour (a–c) reflect within-participant s.e.m.; red bands, 95% CI; ‡significant correlation by bootstrap test; *P<0.05; **P<0.01; +P≤0.10.