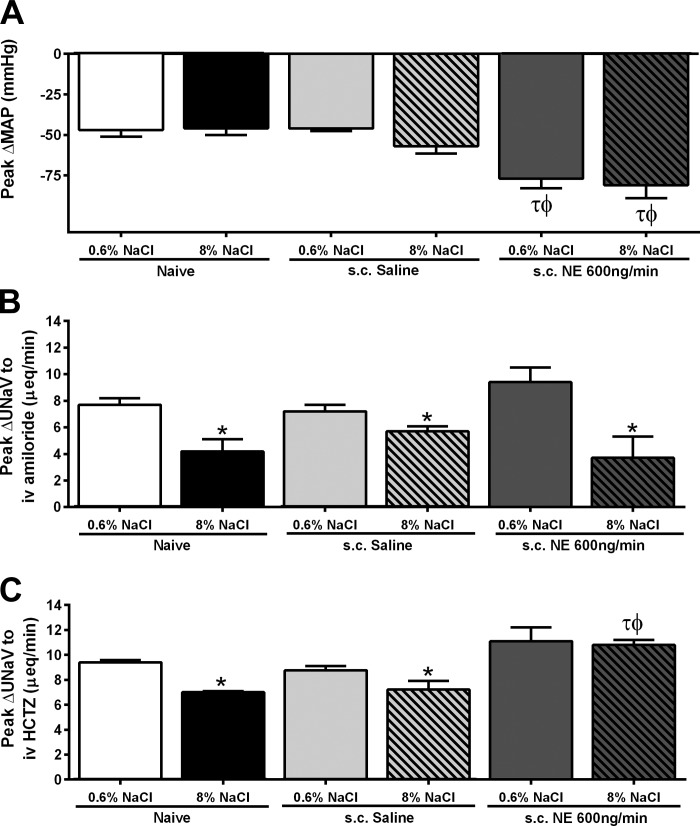
Fig. 2.
A: peak change in MAP (mmHg) in response to an intravenous bolus of hexamethonium (30 mg/kg). B: peak natriuresis (UNaV; μeq/min) in response to an intravenous amiloride infusion (2 mg/kg). C: peak natriuresis (UNaV; μeq/min) in response to an intravenous infusion of amiloride (2 mg/kg) in combination with hydrochlorothiazide (HCTZ; 2 mg/kg), in naïve conscious male Sprague-Dawley rats and in Sprague-Dawley rats receiving either a subcutaneous isotonic saline infusion or a subcutaneous NE (600 ng/min) infusion maintained on either a normal (0.6% NaCl) or high-salt (8% NaCl) diet for 14 days. Data are expressed as means ± SE (n = 6/group). *P < 0.05 vs. respective 0.6% NaCl group value; τP < 0.05 vs. respective naive group value; ϕP < 0.05 vs. respective saline group value.