Figure 4. Rapid disintegration of TE-11R cell membranes after exposure to EGFR(2R)-lytic hybrid peptide in vitro.
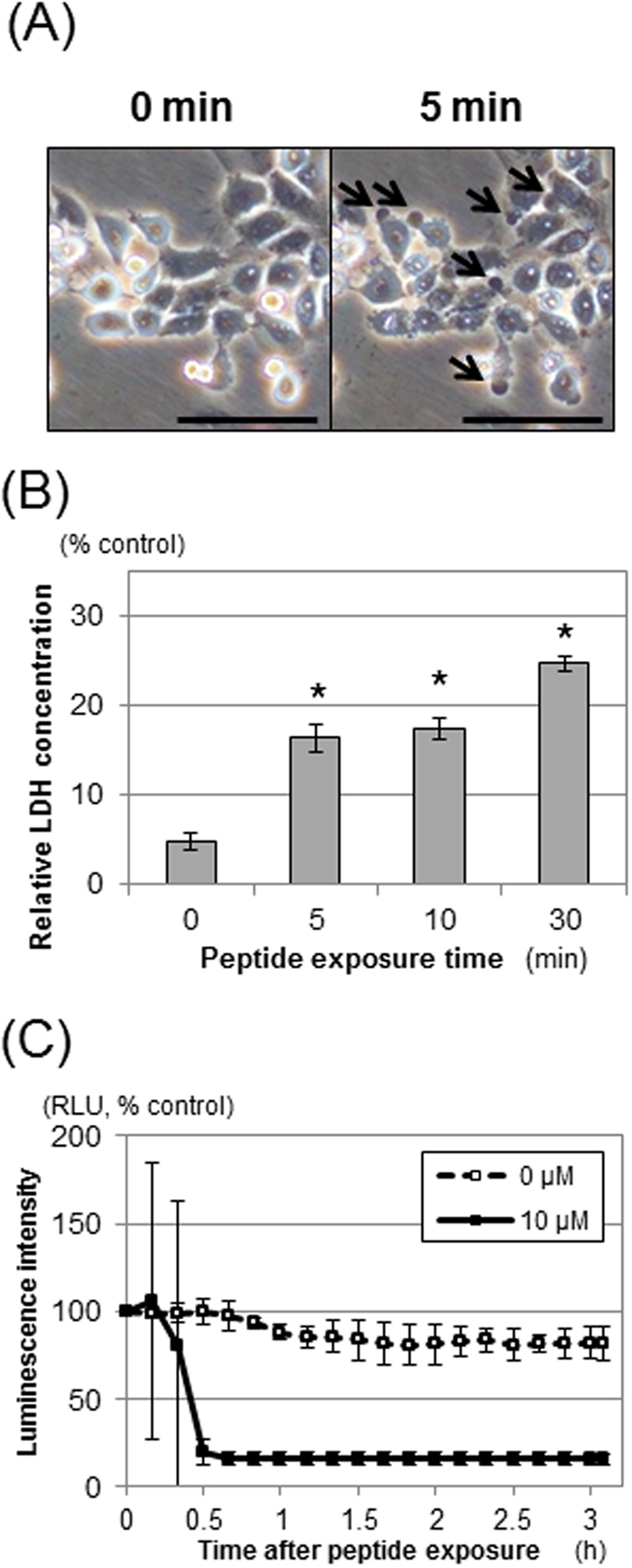
(A) Phase-contrast images of TE-11R cells after exposure to EGFR(2R)-lytic hybrid peptide (10 μM). Extravasation from cell membranes (arrows) occurred at 5 minutes after exposure to EGFR(2R)-lytic hybrid peptide. Scale bar, 100 μm. (B) Extracellular LDH concentrations in culture medium after exposure to EGFR(2R)-lytic hybrid peptide. The relative LDH concentration (% of positive control with Triton X-100) was calculated. A time-dependent increase of extracellular LDH levels was found after exposure to EGFR(2R)-lytic hybrid peptide (10 μM). Each point represents the mean ± S.D. (bars) from experiments conducted in sextuplicate. *P < 0.001 vs. untreated (0 minutes) cells. (C) The real-time cytotoxicity determined by ATP levels in TE-11R cells treated with EGFR(2R)-lytic hybrid peptide. TE-11R cells were transiently transfected with pGL4.50 vector and exposed with (right panel) or without (left panel) EGFR(2R)-lytic hybrid peptide (10 μM) for the indicated durations. Each point represents the mean ± S.D. (bars) from three cells. Note that rapid elimination of ATP was observed in the cells treated with EGFR(2R)-lytic hybrid peptide, but not in those treated without the peptide. These results indicate the rapid disintegration of the cell membrane and consequent cell death after exposure to EGFR(2R)-lytic hybrid peptide.
