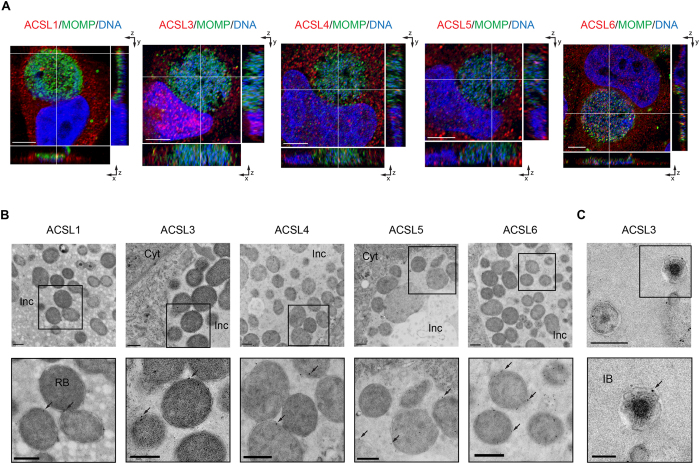
Figure 1. ACSLs are translocated into the C. trachomatis (Ct) inclusion during infection.
(A) HeLa cells were infected with Ct L2 and fixed at 24 hpi. The inclusion was labeled with anti- Ct MOMP antibody (green), ACSL-specific antibodies (red), and Hoechst for nuclear and bacterial DNA (blue) (see Methods). Representative images of z-stack projections from confocal microscopy are shown. White lines indicate localization of the ACSLs inside the inclusion in the three planes, x, y, and z. Scale bar, 5 μm; (B) HEp2 cells were infected with Ct L2 for 24 h, and prepared for TEM. ACSLs were labeled with specific primary antibodies and secondary antibodies conjugated to 12 or 18 nm gold particles (see Methods). The Ct inclusion is shown in the upper panel and an inset at higher magnification in the lower panel. Arrows indicate the gold immunolabeling of respective ACSLs. Inc, inclusion; Cyt, cytoplasm. Scale bar, 500 nm; (C) HEp2 cells were infected with Ct L2 for 24 h and labeled with an anti-ACSL3 antibody as above. A portion of the Ct inclusion is shown on the top panel (scale bar, 500 nm) and a higher magnification inset on the bottom panel. IB, intermediate body. Scale bar, 200 nm.