Figure 8. Model of fatty acid (FA) activation by C. trachomatis (Ct) using host ACSLs.
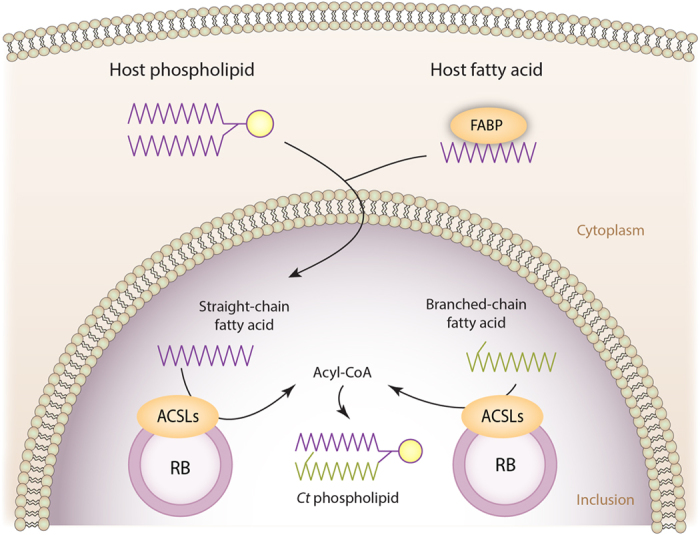
Ct is able to recruit host-cell ACSLs and host straight-chain FAs into the chlamydial inclusion, and synthetize its own branched-chain FAs iso-C15:0 and anteiso-C15:0. FAs must be activated to acyl-CoA before they can be incorporated into phospholipids. Because acyl-CoA is not able to cross the inclusion membrane, activation must occur inside the chlamydial inclusion. We propose that host ACSL1, 3, 4, 5 and 6 are recruited into the chlamydial inclusion to activate both host straight-chain FAs and Ct branched-chain FAs.
