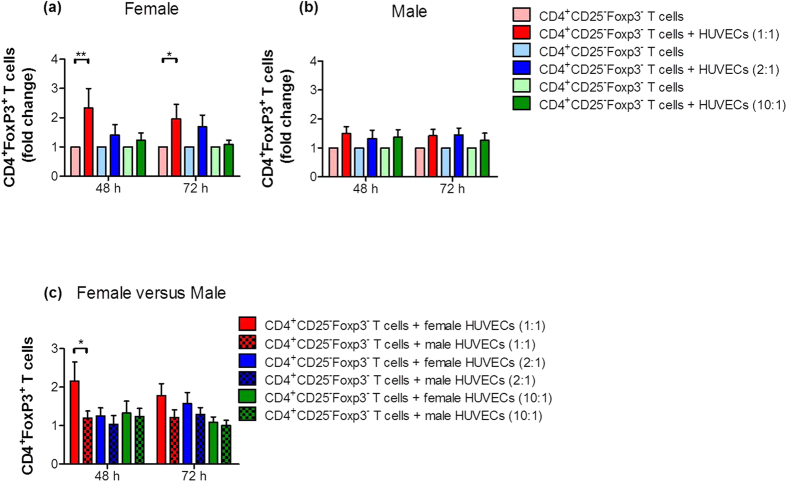
Figure 2. HUVECs induced Treg cell differentiation from CD4+ T cells.
CD4+CD25−Foxp3− T cells were co-cultured with primary female or male HUVECs at cell-to-cell ratios of 1:1; 2:1 and 10:1 (T cells:HUVECs). After 48 and 72 hours, the number of CD4+Foxp3+ T cells was analyzed. HUVECs of both sexes induced Treg cell generation. However, Treg cell number was significantly increased only in co-cultures with female HUVECs (a) at a cell-to-cell ratio of 1:1 at both time points, while male HUVECs (b) stimulated only a slight increase. Results are presented as fold change of controls (T cells cultured alone). Comparison between both sexes revealed a significant stronger potential of female HUVECs to induce Treg cells compared to male cells (c). Samples from 16 normal pregnant women were analyzed in duplicates. Data are presented as means ± S.E.M. Statistical analysis among groups was performed using Two-way-ANOVA followed by Bonferroni correction for multiple comparisons. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01.