Figure 2. Histopathological examination of kidney tissue by HE staining.
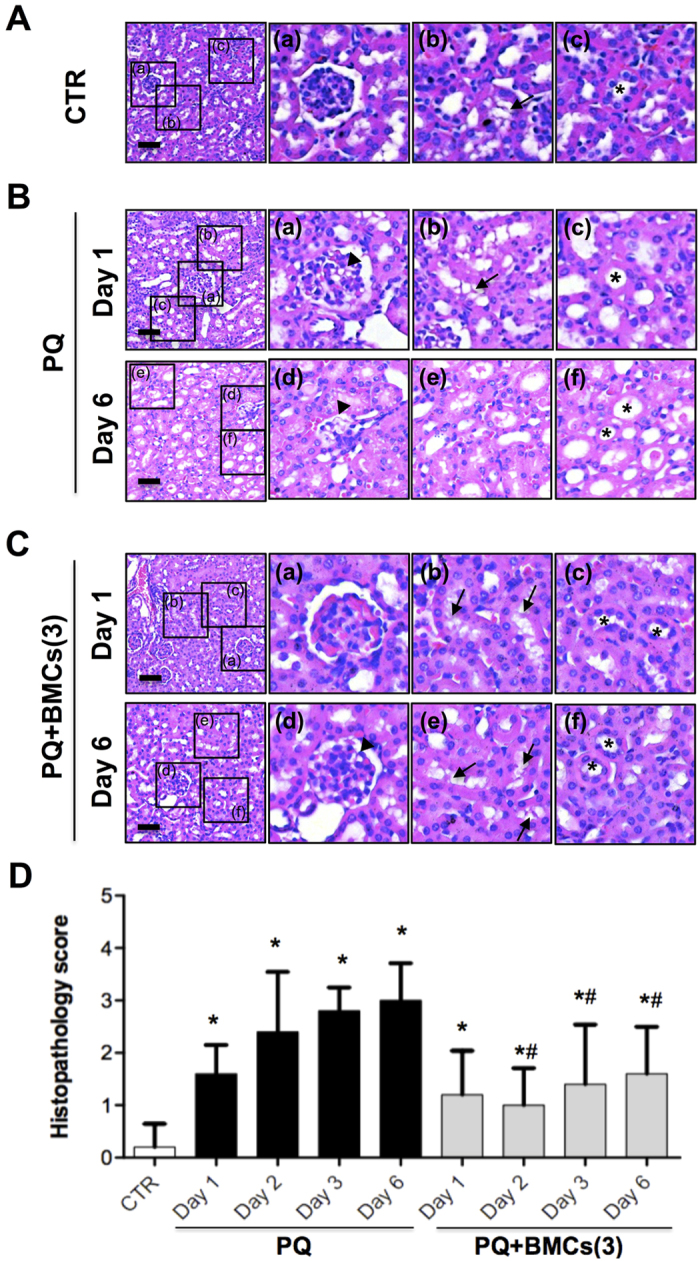
(A) The control group displayed standard kidney histopathology. a, Complete Bowman’s capsule and glomerulus architecture. b, Renal tubule with distributed brush border (arrow). c, Regular nuclear arrangement in renal tubule (asterisk). (B) The PQ-only group displayed histopathological changes. On day 1, kidneys showed mild changes: a, incomplete Bowman’s capsule with vacuolization in the glomerulus (arrowhead); b, mild loss of brush border in the renal tubule; and c, loss of polarity of tubular cells. On day 6, kidneys showed severe histopathological change: d, glomerular shrinkage and decreased space between the glomerulus and Bowman’s capsule (arrowhead); e, loss of brush border in the renal tubule, along with cytoplasmic flattening and loss of the epithelial cells; and f, loss of polarity of tubular cells and degeneration in the renal tubule (asterisk). (C) Triple BMCs administration improved kidney histopathology following PQ treatment. a and d, Complete Bowman’s capsule and glomerulus architecture on day 1 and mild vacuolization in the glomerulus on day 6 (arrowhead). b and e, Renal tubule with distributed brush border (arrows). c and f, Regular nuclear arrangement, and well-development renal tubule (asterisk). Scale bar is 50 μm. (D) Histopathological examination of kidney tissue of PQ administrated mice. Histopathology scoring of renal glomerular degeneration and renal tubule necrosis by a veterinary pathologist: grade 0: no injury; grade 1: minimal injury with less than 10% of cells exhibiting degeneration or necrosis; grade 2: mild injury involving 10–25% of cells; grade 3: moderate injury involving 25–40% of cells; grade 4: marked injury involving 40–50% of cells = grade 4; grade 5: severe injury involving greater than 50% of cells. N = 5, *p < 0.05 vs. control group and #p < 0.05 vs. PQ-only group.
