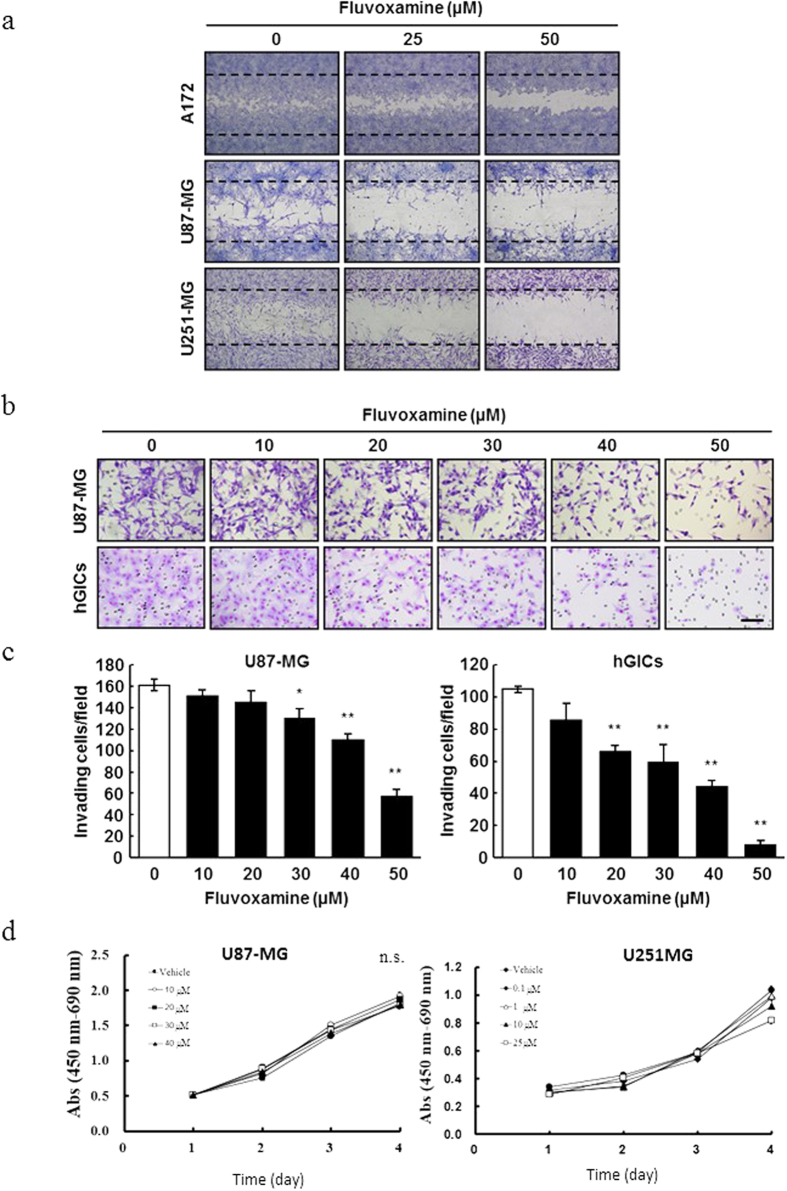
Figure 3. Fluvoxamine inhibited human GBM cell and GIC migration and invasion in vitro.
(a) Fluvoxamine decreased GBM cell migration in a dose-dependent manner. A172, U87-MG, and U251-MG cells were serum-starved for 24 h, treated with fluvoxamine (0, 25, or 50 μM), and processed for wound-healing assay. (b,c) Fluvoxamine inhibited GBM cell invasion in a dose-dependent manner. U87-MG and hGICs were treated with various doses of fluvoxamine and processed for Matrigel invasion assay. Scale bar, 100 μm. Values are mean ± SEM from three independent experiments. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 compared with vehicle, non-repeated measures ANOVA with Dunnett’s post-hoc test. (d) Fluvoxamine did not have no effect to cell proliferation, U87MG and U251MG with WST-1 assay for four days. Values are mean ± SEM from these independent experiments, and statistical analysis was performed using the Student’s T-test by comparing fluvoxamine administrated groups (U87-MG: 10, 20, 30, or 40 μM, U251MG: 0.1, 1, 10, or 25 μM) versus non-treated (vehicle) group . These data showed no significant among these groups in glioma cell proliferation.