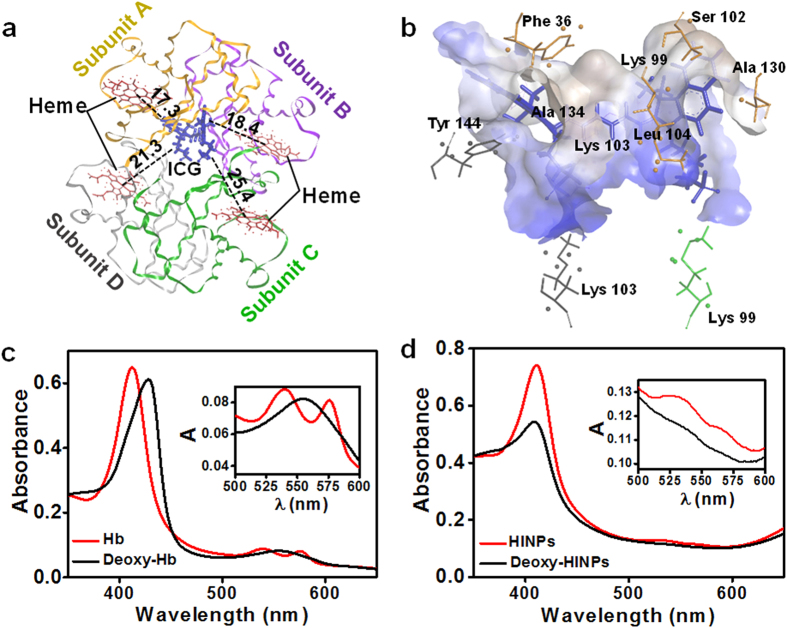
Figure 2. The molecular interaction model of Hb/ICG complex, and characterization of the I-ARCs.
(a) Structural diagram of ICG and Hb complex. Hb consisted of four polypeptide subunits, and ICG molecule bound at the site close to subunit A (yellow) and subunit B (purple) of Hb. ICG was surrounded by 4 hemes, and the oxygens carried on hemes were easily transferred to boosted PDT. (b) The hydrophobic receptor surface was shown as semitransparent surface coloured according to binding properties: blue for hydrophilic and brown for hydrophobic. (c) UV-Vis absorption spectra of deoxy-/oxy- Hb. Inset image in detail showed the characteristic absorption of deoxy-/oxy- Hb. (d) UV-Vis absorption spectra of I-NARCs and deoxygenated I-NARCs. Inset image in detail showed the absorption of deoxy-/oxy- I-NARCs, in which the characteristic absorption changed similarly to that of deoxy-/oxy- Hb. (e) Acidic stability of Hb in I-ARCs. Precipitation occurs in Free Hb solution at pH 6.7, significantly reduced oxygen loading function, while nano-functionalized Hb solution (I-ARCs) kept clear and transparent, proving a wonderful stability under acidic condition. (f) Thermal stability of Hb in I-ARCs, ARCs, or free Hb.