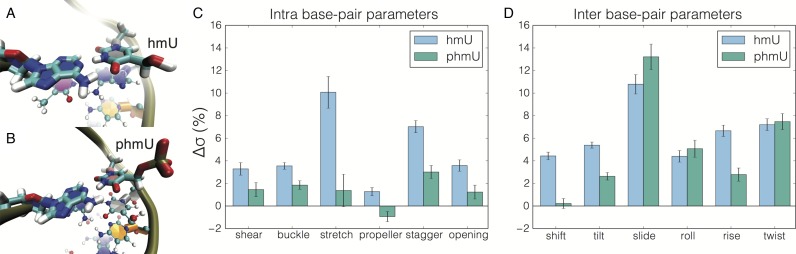
Figure 4.
Results of molecular dynamics simulations characterizing structural fluctuations of the DNA variants. (A, B) Molecular bond representation of the hmU modification (A) and phmU modification (B) within the h-DNA and p-DNA constructs, respectively. (C) Differences in the standard deviation of the intra-base pair parameters for the hmU- and phmU-modified DNA relative to the values obtained for unmodified t-DNA. The h-DNA construct exhibits increased fluctuations in the average base pair geometry. (D) Differences in the standard deviation of the inter-base pair parameters for the h-DNA and p-DNA constructs relative to t-DNA. Both h-DNA and p-DNA show increased inter-base pair fluctuations suggesting that these molecules are more flexible than t-DNA. The relative difference in standard deviation Δσx = 100×(σx – σt)/σt, where σt and σx are the standard deviations of a parameter in t-DNA and x-DNA, respectively (x is either h or p), averaged over the time series and then over base pairs or base pair steps. The error was calculated by splitting MD trajectories of the same chemical system into thirty blocks and calculating the standard deviation within each block for each base pair or step. The standard error of these 30 estimates was then propagated to reflect averaging over all base pairs or steps.