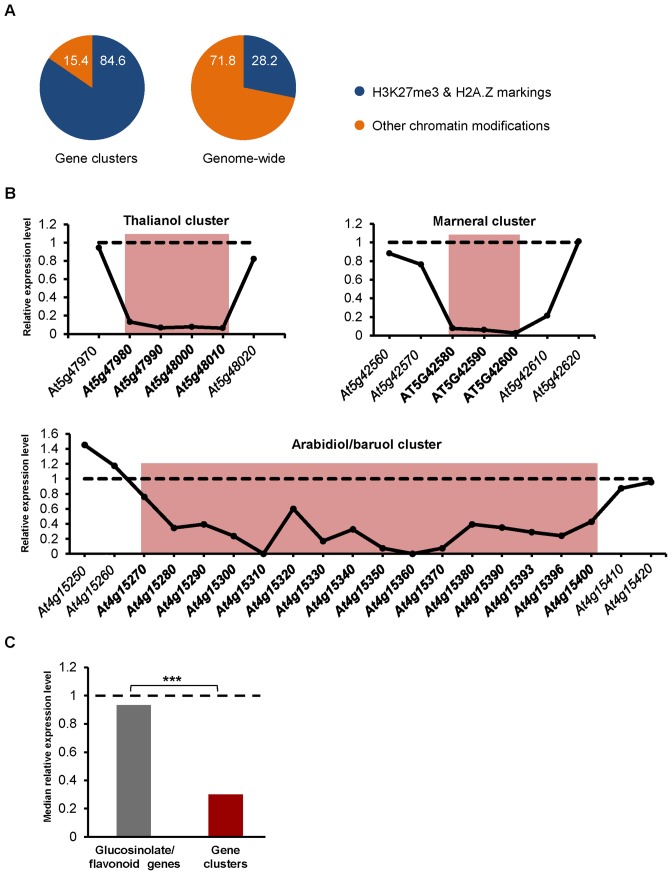
Figure 5.
H3K27me3-marked co-expressed regions are marked by histone variant H2A.Z and show H2A.Z-dependent expression in Arabidopsis thaliana. (A) The seven A. thaliana clusters identified (Supplementary Table S4) are located in genomic regions that have just two predominant chromatin markings—H3K27me3 and H2A.Z. Data were extracted from a genome-wide chromatin map for A. thaliana that covers 16 different chromatin features (44) (Supplementary Figure S6; Supplementary Data Set 6). (B) Relative transcript levels of the thalianol, marneral and arabidiol/baruol cluster genes and flanking genes in the H2A.Z mutant line hta9/11 (solid line) compared to the wild-type (dashed line) as assessed by RNAseq analysis. The cluster genes are indicated in bold and the cluster region highlighted in red. (C) Median relative expression values of genes for the seven A. thaliana clusters identified in Supplementary Table S4 and for the two well characterized non-clustered glucosinolate and flavonoid pathways in the H2A.Z mutant line hta9/11. The dashed line indicates wild-type expression. ***P < 0.001 (Mann–Whitney-U-Test).