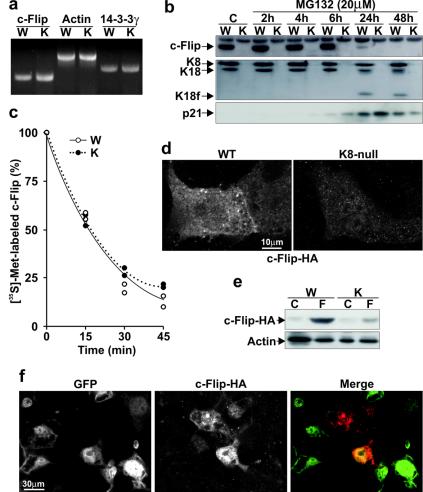
FIG. 4.
c-Flip downregulation in K8-null hepatocytes occurs at the posttranscriptional level. (a) RT-PCR showing no difference in c-Flip mRNA content between WT (W) and K8-null (K) hepatocytes. As controls, no variations are detected in actin and in 14-3-3γ mRNA levels. (b) Proteasome inhibition with 20 μM MG132 does not rescue the c-Flip in K8-null hepatocytes (K) (K18f, fragment of K18). Used as a control, the level of p21 protein increases after MG132 treatment in both WT and K8-null hepatocytes. (c) The disappearance kinetics of [35S]methionine-labeled c-Flip after a pulse-chase point to a comparable turnover in WT and K8-null hepatocytes. (d) HA-tagged c-Flip cDNA transfection shows an increased c-Flip-HA protein content in transfected WT versus K8-null hepatocytes. (e) A Western blot reveals a higher c-Flip-HA protein content in WT (W) than in K8-null (K) hepatocytes after transfection (F) of a c-Flip-HA cDNA; the “C” refers to nontransfected (control) hepatocytes. (f) K8-null hepatocytes infected with a recombinant K8 cDNA-IRES-EGFP cDNA retrovirus, followed by transfection with a c-Flip-HA vector, show that the expression of c-Flip-HA (red in merge image) is stronger in K8 expressing cells (GFP, green in merge image).