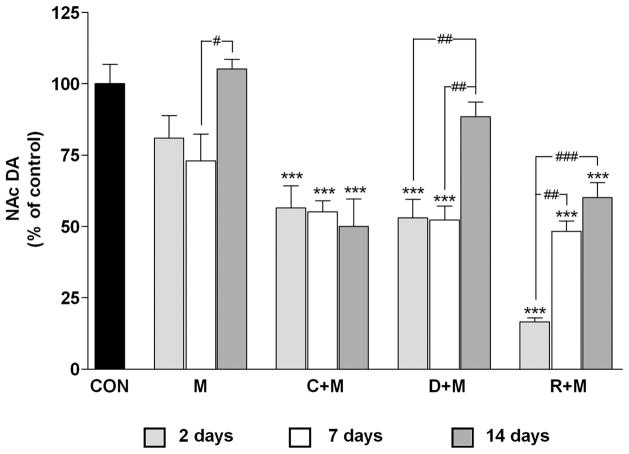
Figure 1.
Effects of a neurotoxic methamphetamine (Meth) regimen on dopamine (DA) depletion in the nucleus accumbens (NAc) when administered alone and in conjunction with clorgyline, L-DOPA, or reserpine. Mice (n = 5–8 per group) were treated with Meth alone (M: 4 × 5 mg/kg; 2 hr between injections) or in conjunction with clorgyline (C + M: 10 mg/kg; t = −1 h), L-DOPA (D + M: 50 mg/kg, t = −1 and 3 hr), or reserpine (R + M: 2.5 mg/kg; t = −24 h). NAc DA levels were measured 2, 7, and 14 days post-Meth. Results are presented as means ± SEM relative to controls (CON). Significant differences were determined via one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) followed by Tukey’s multiple comparison test, and are indicated as follows: **, p < 0.01, and ***, p < 0.001 relative to control; #, p < 0.05, ##, p < 0.01, and ###, p < 0.001 indicate significant differences between indicated treatment conditions. Reprinted with permission from Thomas et al. (2009).