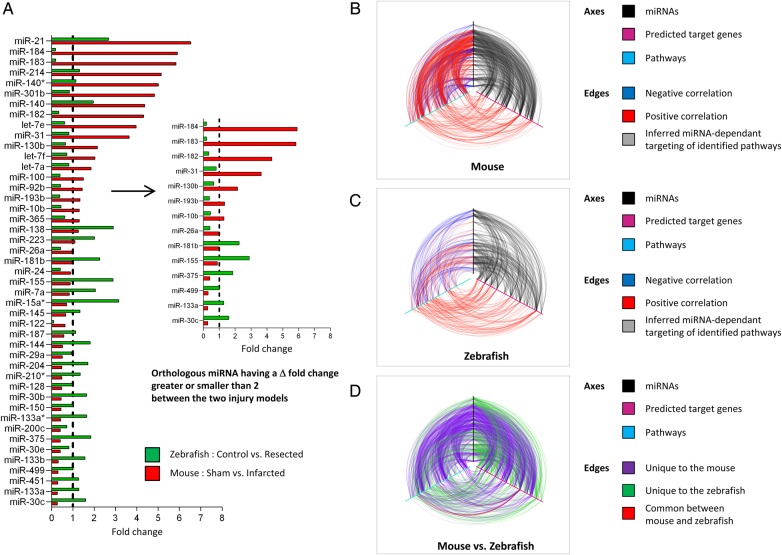
Figure 1.
miRNAs and pathways are differentially utilized in the injured mouse and zebrafish hearts. (A) Differentially utilized subnetworks in the mouse and zebrafish hearts following injury were extracted for further analysis. List of the 45 orthologous miRNAs differentially modulated between the two cardiac injury models. The bar graph represents the fold change in the expression level of the indicated miRNAs in the infarcted mouse heart (red bars) and in the resected zebrafish hearts (green bars), relative to their respective controls (Sham mouse hearts and control zebrafish hearts), in which the expression level is set as 1 (dashed vertical black line). A selection of 14 orthologous miRNAs having a Δ-fold change between the two cardiac injury models greater or smaller than 2 is shown on the right. (B–D) Hive plot representation of differentially expressed miRNAs (black axes), predicted target genes (magenta axes), and pathways (cyan axes) in the injured mouse and zebrafish hearts. (B) Red lines (arcs) indicate positive correlation; blue lines indicate negative correlation. Grey lines indicate targeting of inferred miRNA-dependent pathways. (C) Hive plot representation of differentially expressed miRNAs, mRNAs, and pathways in the resected zebrafish heart. Red lines indicate positive correlation; blue lines indicate negative correlation. Grey lines indicate targeting of inferred miRNA-dependent pathways. (D) Hive plot representation of miRNA, mRNA, and pathway relationships unique to the mouse (purple) or to the zebrafish (green). Red lines indicate relationships common to mouse and zebrafish. See also Supplementary material online, Figure S1–S4 and Table S1–S6.