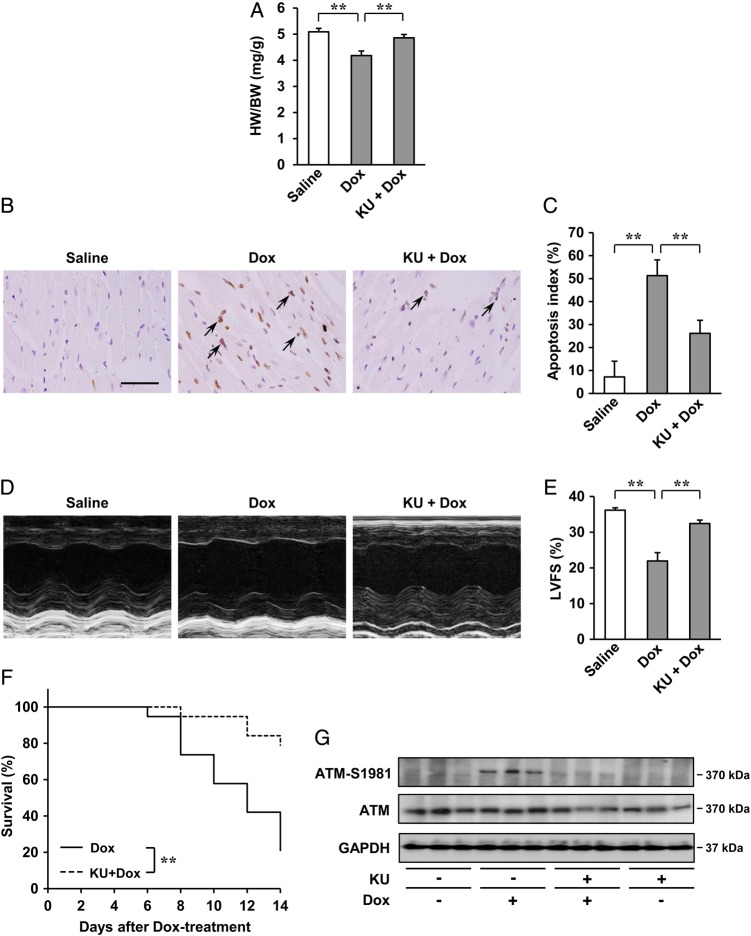
Figure 6.
Effects of ATM inhibitor, KU55933 (KU), on Dox-induced cardiotoxicity in vivo after 2 weeks. (A) HW/BW ratio (n = 5 per group). (B and C) Dox-induced cardiac apoptosis as assessed by TUNEL staining. Immunoreactivity was visualised with diaminobenzidine (brown). Haematoxylin was used as nuclear stain (blue). Arrows indicate TUNEL-positive cardiac cells (B). Scale bar: 50 µm. Apoptosis index (percentage of TUNEL-positive nuclei) was calculated as TUNEL-positive nuclei/total nuclei × 100 (%). Apoptosis index of cardiac cells was plotted (n = 3 per group, total of 18 visual fields) (C). (D and E) Echocardiographic analysis (n = 5 per group). M-mode echocardiographic tracings (D) and LVFS of mice (E) treated with saline or Dox, or KU55933 + Dox. The results are expressed as means ± SD; **P < 0.01 by one-way ANOVA followed by a post hoc Tukey's multiple comparisons test. (F) Kaplan–Meier survival analysis of C57BL/6 mice 2 weeks after treatment with Dox (n = 19) and C57BL/6 mice treatment with KU55933 + Dox (n = 19). **P < 0.01 by log-rank test. (G) Expression of ATM (S1981) and ATM examined by western blot analysis. GAPDH was used as the loading control.