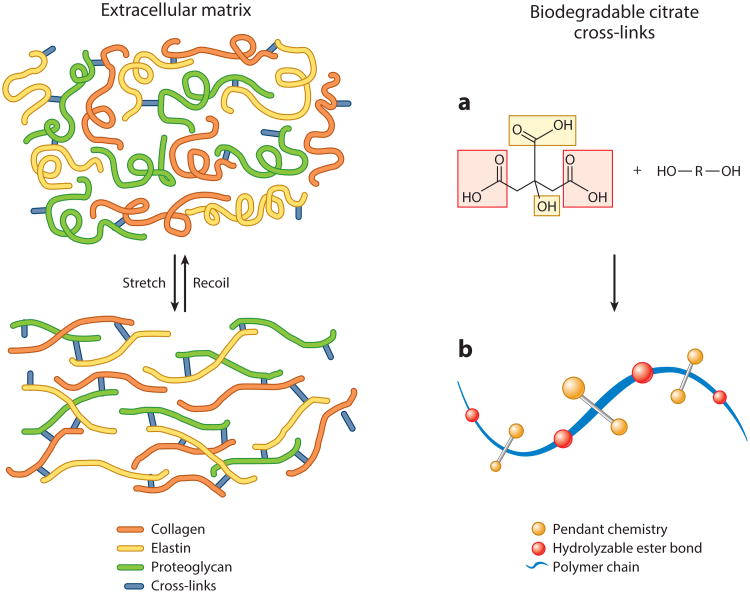
Figure 2.
Representative simplified schematic of the native extracellular matrix cross-linked network structure that inspired the design for thermoset biodegradable elastomers. (a) The multifunctionality of citric acid provides several reaction sites for prepolymer chain elongation (red) while preserving pendant chemistry for subsequent cross-linking or polymer modification (yellow). (b) Reacting citric acid with diol monomers produces degradable ester bonds (red) while preserving pendant carboxyl and hydroxyl chemistry (yellow) in the bulk of the material, which can be used for subsequent polymer chain cross-linking or material surface modification.