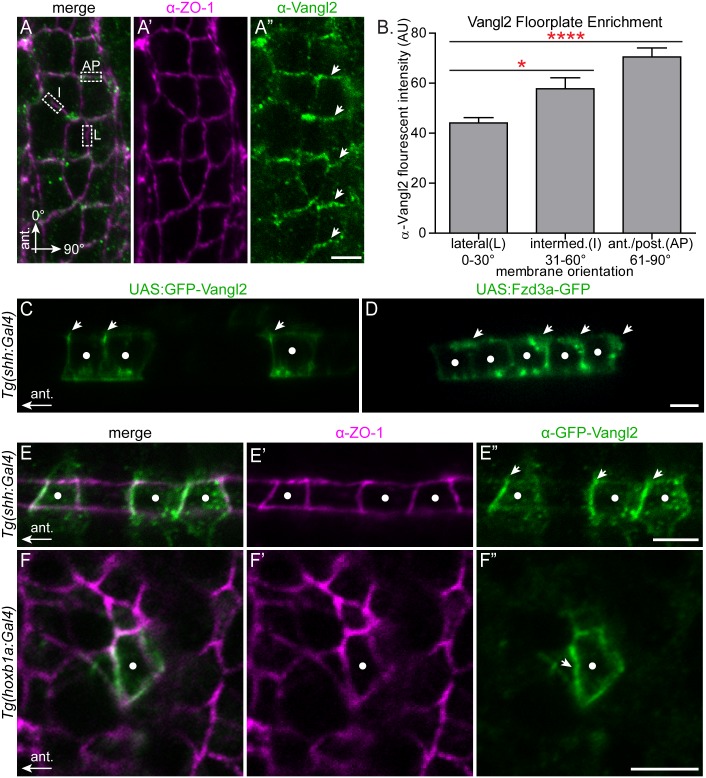
Fig 4. Polarization of PCP protein localization in the migratory environment.
(A-A”) Dorsal view with anterior to the top of a 24 hpf wild type floorplate at the level of r4 co-immunostained with anti-Vangl2 (green) and anti-ZO-1 (magenta), a marker of apical tight junctions. The boxed regions in A are examples of anterior-posterior membranes (AP) (61–90° from AP axis), intermediate membranes (I) (31–60° from AP axis) and lateral membranes (L) (0–30° from AP axis). Arrows in A” indicate enrichment of anti-Vangl2 labeling at AP membranes. (B) Quantitation of fluorescent intensity of anti-Vangl2 labeling for AP, I and L membranes. N = 5 embryos, 192 membranes (57 L, 47 I, 88, AP). Graph represents data as mean ± SEM. *p = 0.018, ****p<0.0001; Significance was determined using a paired two-tail t-test with Welch’s correction. (C-D) Live lateral views of 48 hpf wild type floorplate cells at the level of the spinal cord with mosaic expression of GFP-Vangl2 (C) and Fzd3a-GFP (D). Anterior is to the left and dorsal/apical is up; white dots indicate the center of each expressing floorplate cell, arrows indicate anterior subapical membrane enrichment of GFP-Vangl2 (C) and posterior subapical enrichment of Fzd3a-GFP (D). (E-E”) Dorsal view of the apical surface of floorplate cells in a 48 hpf embryo expressing GFP-Vangl2 (green) and stained for ZO-1 (magenta) Anterior is to the left; white dots indicate the center of the expressing cell. Arrows in E” indicate anterior enrichment of GFP-Vangl2. (F-F”) En face view of the apical endfeet of neuroepitheilial cells in r4 of a 24 hpf embryo expressing GFP-Vangl2 (green) and stained for ZO-1 (magenta). Anterior is to the left; white dot indicates the center of the expressing cell. Arrow in F” indicates anterior enrichment of GFP-Vangl2. N = 17 embryos, 23 cells. Scale bars: 5 μm.