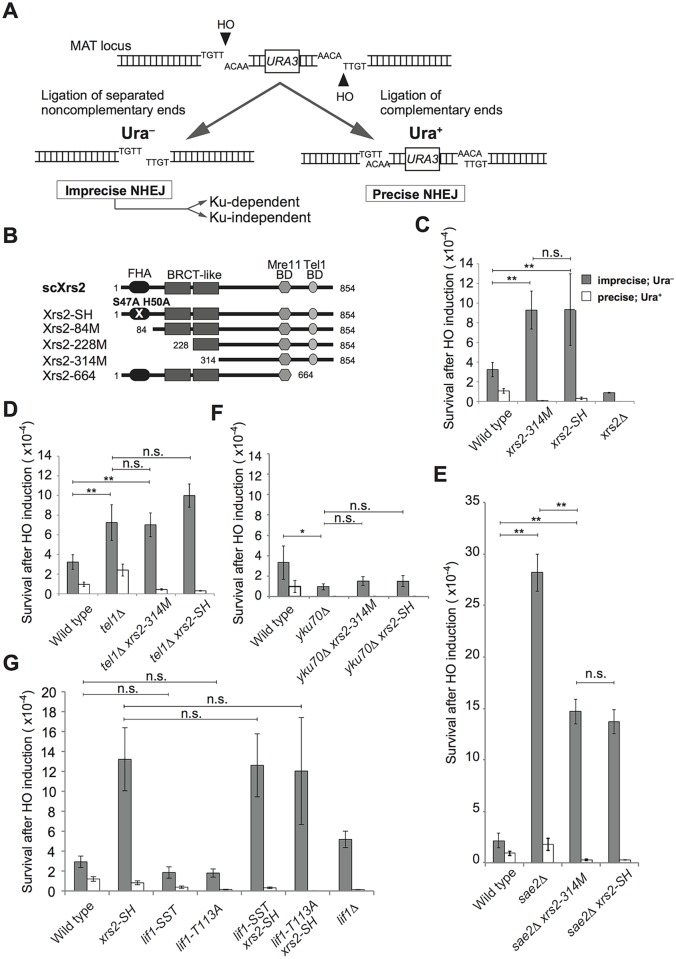
Fig 1. Imprecise end joining increased in cells with Xrs2 FHA domain mutations in a Tel1-dependent manner.
A. System used to examine imprecise end joining. Two HO-cutting sites were introduced in opposite orientations within the MAT locus on chromosome III, that result in two kinds of DSB ends: non-complementary single-stranded over hangs (Ura−) and complementary overhangs (Ura+), which are repaired by imprecise end joining and precise end joining, respectively. B. Xrs2 protein domains for wild-type and mutant Saccharomyces cerevisiae (sc) proteins. Mre11 BD, Mre11-binding domain; Tel1 BD, Tel1-binding domain. C. Frequencies of Ura− and Ura+ cells indicate imprecise end joining and precise end joining, respectively, in wild-type (SLY19), xrs2-314M (DIY002), xrs2-SH (DIY016) and xrs2Δ (DIY007) strains. D. End-joining frequencies in wild-type, tel1Δ (DIY129), tel1Δ xrs2-314M (DIY131) and tel1Δ xrs2-SH (DIY134) strains assessed as in C. E. End-joining frequencies in wild-type, sae2Δ (DIY059), sae2Δ xrs2-314M (DIY062) and sae2Δ xrs2-SH (DIY065) strains assessed as in C. F. End-joining frequencies in wild-type (SLY19), yku70Δ (DIY033), yku70Δ xrs2-314M (DIY051) and yku70Δ xrs2-SH (DIY048) strains assessed as in C. G. End-joining frequencies in wild-type, xrs2-SH (DIY134), lif1-SST (DIY027), lif1-T113A (DIY072), lif1-SST xrs2-SH (MSY5655), lif1-T113A xrs2-SH (MSY5652) and lif1Δ (KMY691) strains assessed as in C. The wild-type data in C, D and E are from a single experiment. Data are presented as the mean ± SD from three independent experiments. Significance was calculated with a Student’s t-test: **p<0.001; *p<0.05; n.s., not significant.