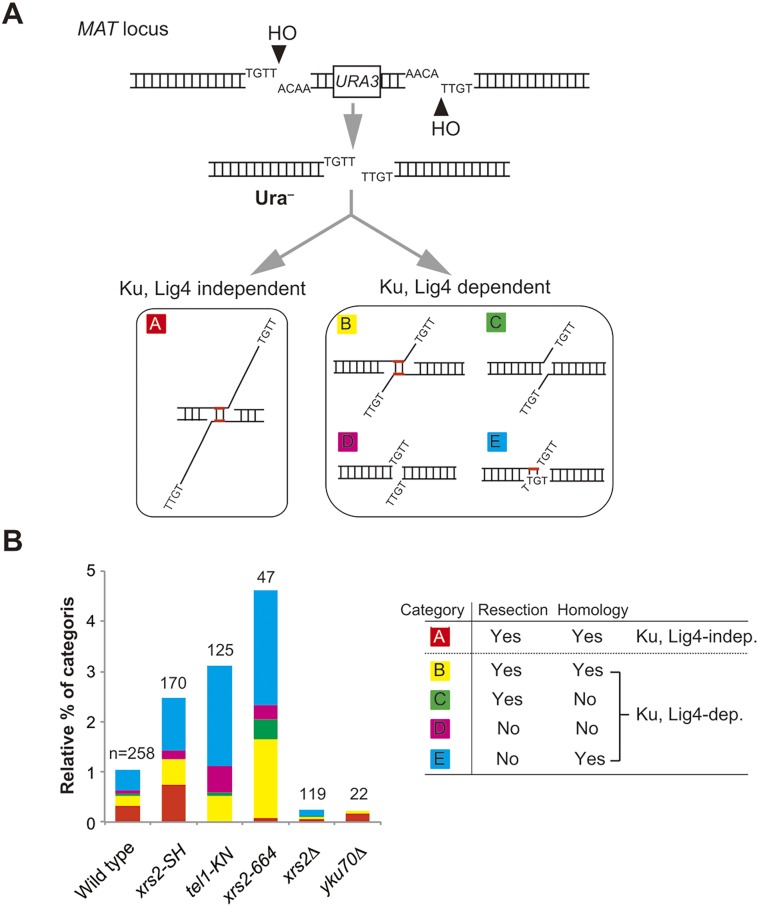
Fig 2. Distribution of DSB repair types produced by non-complementary DSB repair.
A. The assay system and classification of the repair type depend on the junction analysis. Repaired products generated by survivors shown in Fig 1C and others were classified into five categories. Category A: repaired by annealing of microhomology with large asymmetric resection of up to 60 nucleotides in a Ku- and DNA ligase IV (Lig4)-independent manner. Category B: repaired by end joining mediated by annealing of microhomology with resection. Category C: repaired by end joining without microhomology-mediated annealing at resected ends. Category D: repaired by end joining without microhomology-mediated annealing and end resection. Category E: repaired by end joining with microhomology-mediated annealing without resection. Categories B–E are Ku and DNA ligase IV dependent. B. Distribution of each category of repair type in various strains. Left: Frequency of each category shown in A of the imprecise–end joining categories in wild type (SLY19), xrs2-SH (DIY016), tel1-KN (MSY4629), xrs2-664 (MSY4835), xrs2Δ (DIY007) and yku70Δ (DIY033). Numerical values are shown in S3 Table. Right: Summary of classification of each category. n, number of samples analyzed for each strain.