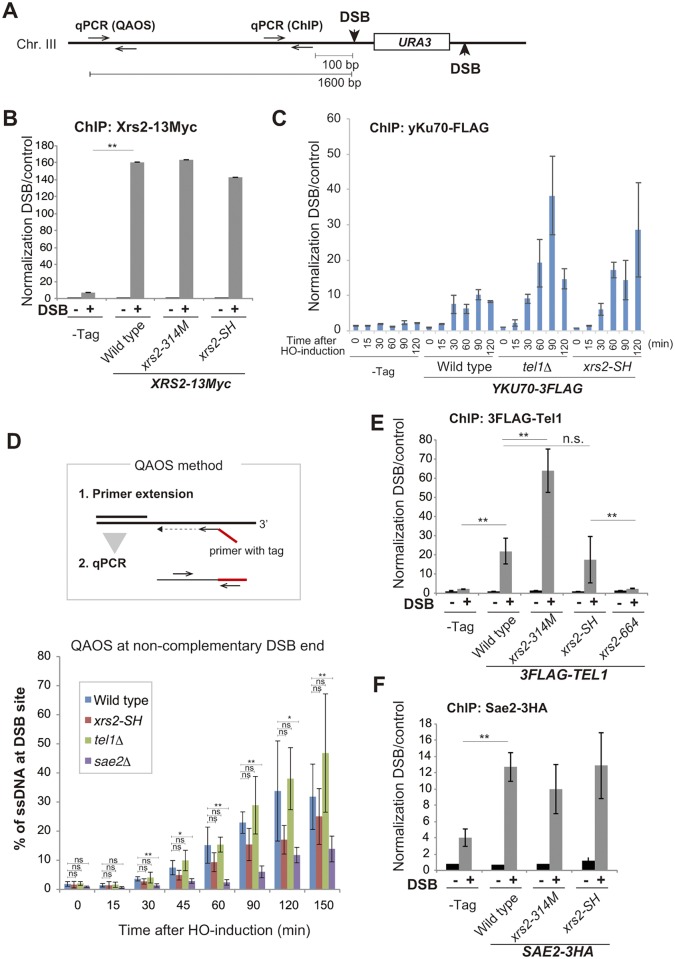
Fig 3. Recruitment of DDR proteins to non-complementary DSB ends.
A. Construction of DSB sites at the MAT locus on chromosome III of strain SLY19 and position of the primer pair for qPCR for ChIP analysis and QAOS assay. B. The association of Xrs2 protein with DSBs in SLY19 (–Tag) or in its derivatives with XRS2-13Myc (wild type, DIY109; xrs2-314M, DIY116; xrs2-SH, DIY106). Error bars show the SD from three independent qPCR trials. C. Time course analysis of the association of yKu70 protein with DSBs in SLY19 (–Tag) or in its derivatives with YKU70-3FLAG (wild type, MSY4829; tel1Δ, DIY118; xrs2-SH, DIY120). Data are presented as the mean ± SD from four independent trials. Significance was calculated with a Student’s t-test: **p < 0.001; *p < 0.05; n.s., not significant. D. The QAOS method is shown (upper). ssDNA at DSB ends was detected by QAOS assay in wild type (SLY19), xrs2-SH (DIY016), tel1Δ (DIY129) and sae2Δ (DIY059) cells. Data are presented as the mean ± SD from three independent experiments. Significance was calculated with a Student’s t-test: **p < 0.001; *p < 0.05; n.s., not significant. E. The assembly of Tel1 protein on DSBs in SLY19 (–Tag) or in its derivatives with 3FLAG-TEL1 (wild type, MSY5505; xrs2-314M, MSY5539; xrs2-SH, MSY5486; xrs2-664, MSY5541). F. Association of Sae2 protein with DSBs in SLY19 (–Tag) or in its derivatives with SAE2-3HA (wild type, DIY142; xrs2-314M, DIY144; xrs2-SH, DIY146). In B and F or E, a ChIP assay was performed at the HO cutting site at 150 or 120 min, respectively, after HO induction (DSB +) or before induction (DSB–). Error bars in C, E and F show the SD from three or more independent experiments, each of which consisted of an average from three independent qPCR trials for each strain.