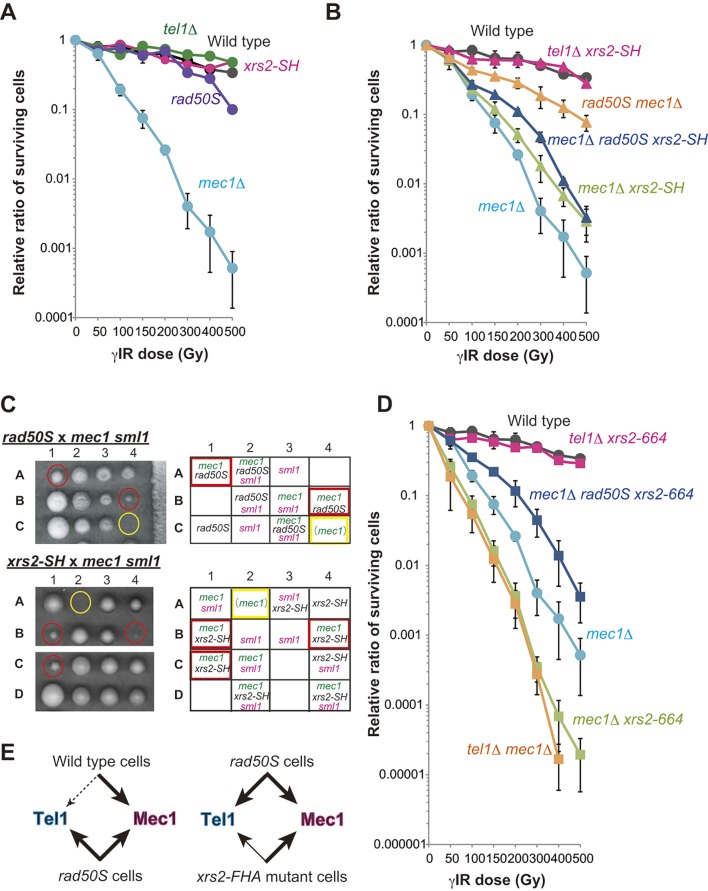
Fig 4. The FHA mutation partially up-regulates Tel1 and suppresses robust activation of Tel1 in the rad50S background.
A. Survival of yeast cells after γIR of wild-type (W303-1A), xrs2-SH (MSY2199), tel1Δ (MSY2175), rad50S (MSY2203) and mec1Δ sml1Δ (shown as mec1Δ; MSY2211) cells. B. Survival after γIR of wild-type (W303-1A), mec1Δ xrs2-SH (MSY2331), tel1Δ xrs2-SH (MSY2319), rad50S mec1Δ (MSY2461), mec1Δ rad50S xrs2-SH (MSY2372) and mec1Δ (MSY2211) cells. C. Tetrad analysis of rad50S mec1Δ sml1Δ heterozygotes (MSY2205 × MSY2211; upper panel) and xrs2-SH mec1Δ sml1Δ heterozygotes (MSY2201 × MSY2211; lower panel). The genotypes of each dissected colony are shown. Red circles and rectangles indicate suppression of mec1 lethality without the sml1 mutation. Yellow circles and rectangles indicate inviable colonies that were presumed to be mec1Δ cells based on the segregation pattern of the tetrads. D. Survival after γIR of wild-type (W303-1A), mec1Δ xrs2-664 (MSY2309), tel1Δ xrs2-664 (MSY2327), rad50S mec1Δ xrs2-664 (MSY2356), tel1Δ mec1Δ (MSY2481) and mec1Δ (MSY2211) cells. The data shown in A, B, and D with the same label are based on the same set of experiments (that is wild type, mec1Δ). Error bars show the SD from three independent experiments. E. Conclusions from the irradiation analysis and tetrad analysis. The thickness of the arrow and the size of the arrowhead show the strength of the DDR in the indicated strains. Whereas Mec1 functions mainly in wild type, the rad50S mutation activates Tel1 activity (left). In contrast, an FHA mutation of xrs2 only partially activates Tel1 activity in the rad50S background (right).