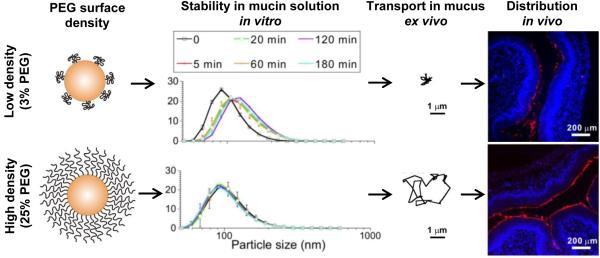
Figure 4.
The impact of PEG surface density on interactions with mucus in vitro, ex vivo, and in vivo. A polymer blending approach was used to produce biodegradable PLGA NPs of similar size with increasing PEG surface densities. Above a certain threshold (5% target PEG content for this formulation), NPs were more stable in mucin solution in vitro, diffused rapidly in human cervicovaginal mucus ex vivo, and distributed more uniformly over the vaginal surface of mice in vivo. A dense PEG coating protected the NP surface from interactions with mucus, leading to more uniform delivery to the mucosal surface. Adapted with permission from [135].