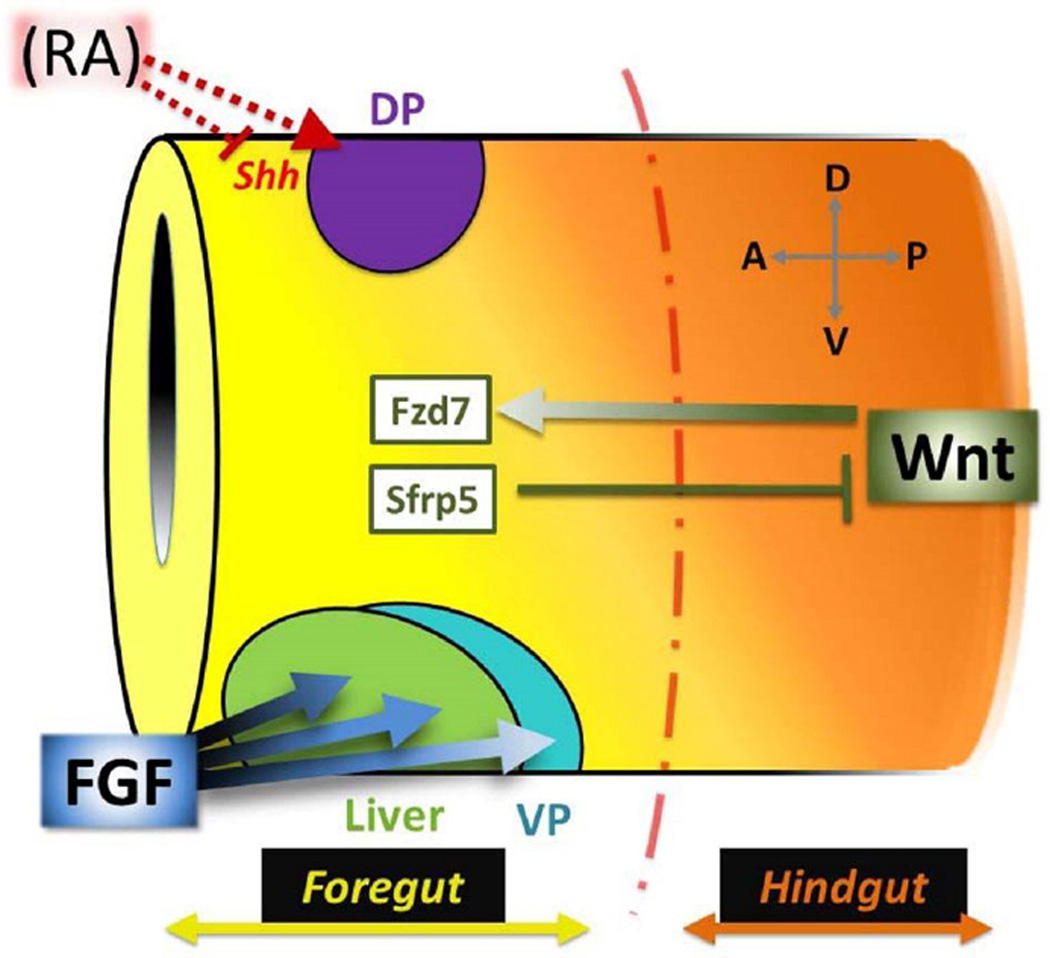
Figure 1. Wnt, RA, and FGF pattern the foregut.
The primitive gut tube is regionalized along both A–P and D–V axes. During gastrulation, RA (red) is required for dorsal pancreas (DP; purple) specification, likely by inhibiting Shh expression. Slightly later, the foregut is distinguished from the hindgut by a gradient of Wnt signaling (orange). High posterior Wnt specifies the hindgut domain, while low anterior Wnt (yellow; limited by Sfrp5) signals through the Fzd7 receptor to promote foregut fates and initiate cellular morphogenesis. Finally, a gradient of FGF signaling from the neighboring cardiac/lateral plate mesoderm segregates ventral foregut organs; prolonged, higher levels of FGF are needed to specify liver (green) versus ventral pancreas (VP; blue).