Figure 4. Functional configurations of multisensory integration at the mossy fiber–granule cell connection.
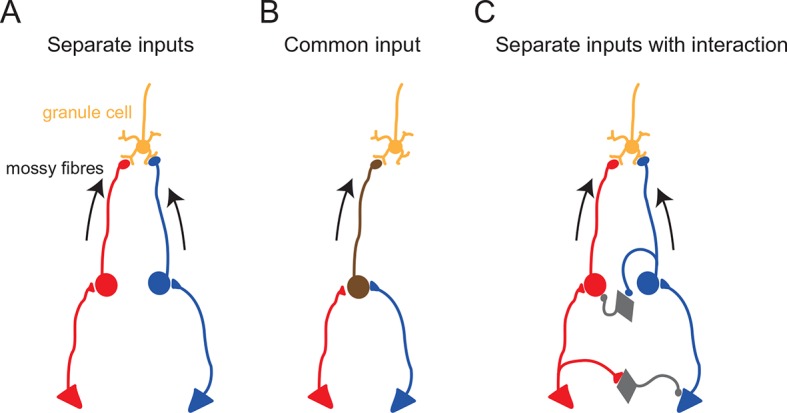
Schematic diagrams showing potential anatomical substrates of the different multisensory integration scenarios described in the results. (A) Multimodal signals are transmitted by separate pathways and converge onto a single granule cell. (B) A single mossy fiber conveys mixed multi-modal signals. (C) Multimodal signals converge onto a granule cell, but the two pathways interact. In these schematics, the round cells represent pre-cerebellar neurons whose axons form mossy fibers. The triangular cells represent neurons projecting to the pre-cerebellar neurons (e.g. cortical neurons projecting to pontine neurons). Gray diamond-shaped neurons represent hypothetical interneurons. Another possibility for interaction between two separate pathways (not illustrated here) is presynaptic inhibition (Mitchell and Silver, 2000) or postsynaptic inhibition (Duguid et al., 2015) via Golgi cells.
