Figure 1.
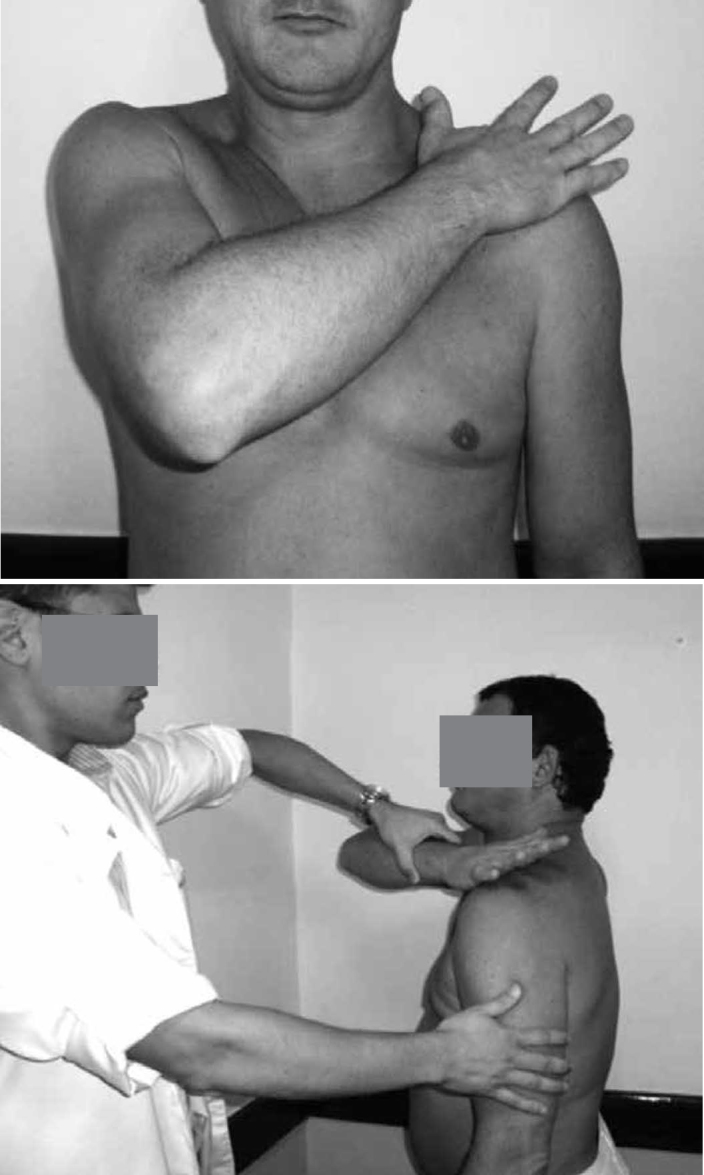
Bear hug semiological maneuver as described by Barth et al(13). The patient is placed in an upright standing position. The hand ipsilateral to the affected shoulder is positioned on the contralateral shoulder with the fingers stretched out and the elbow positioned anteriorly to the body. The patient is asked to maintain this position (resisted internal rotation) while the examiner tries to perform external rotation by applying a force on the forearm so as to remove the patient's hand from his shoulder. If the patient is unable to keep his hand on his shoulder, or the resistance is 20% lower than on the contralateral side, the test is considered to be positive. If the force is equivalent to that of the opposite side and pain is absent, the test is defined as negative.
