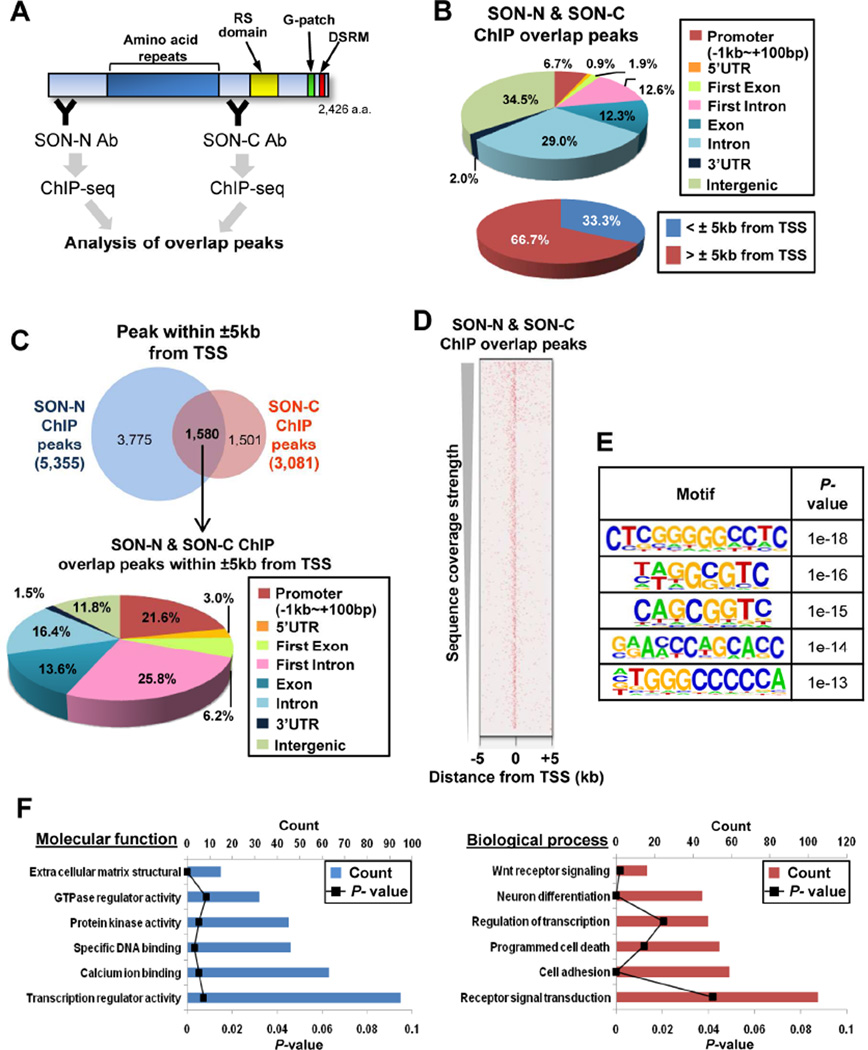
Figure 1. The Genome-Wide Distribution Profiles of SON DNA-Binding Sites.
(A) A schematic summarizing chromatin-immunoprecipitation (ChIP) using two different SON antibodies (Abs) and DNA-sequencing to determine overlap peaks. SON-N and SON-C Abs specifically bind to the N- and the C-terminus of SON, respectively. RS domain, Ser/Arg-rich domain; G-patch, Glycine-rich motif; DSRM, double stranded RNA-binding motif.
(B) Genomic distribution of SON-binding sites determined by SON-N and SON-C ChIP overlap peaks. The pie graphs show the percentage of peaks located at specific genomic regions indicated (TSS, transcription start site).
(C) Venn diagram showing the number of SON ChIP peaks (SON-N, SON-C and overlap) within ±5kb from the TSS (Top). Pie graph illustrating genomic locations of overlap peaks within ±5kb from the TSS (Bottom).
(D) The heat map showing the overlap peak signal of SON ChIP around the TSS of genes.
(E) The top five DNA sequence motifs identified in the SON-N and SON-C overlap peaks within ±5kb of the TSS.
(F) Gene ontology (GO) term enrichment analysis using DAVID for the genes in which SON-N and SON-C overlap peaks are found within ±5kb from the TSS. See also Figures S1 and S2.