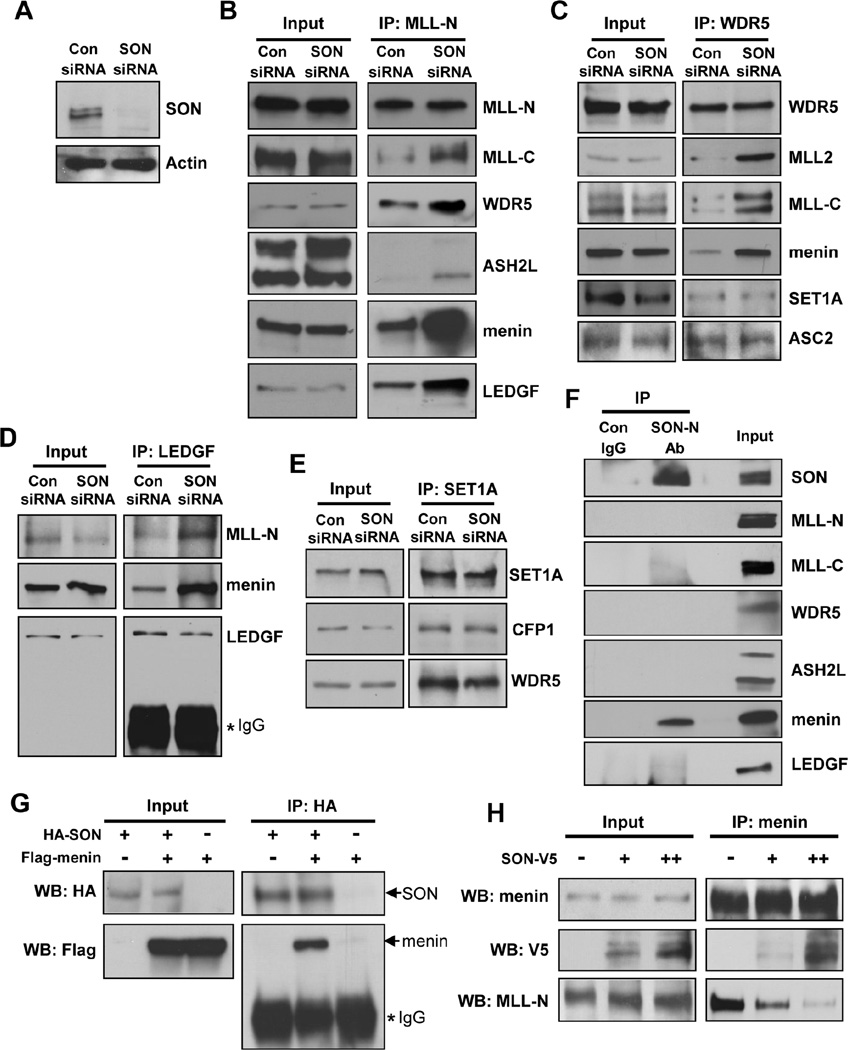
Figure 4. SON Suppresses MLL1/2 Complex Formation by Competing with MLL for Menin Interaction.
(A) Western blot verified SON knockdown by SON siRNA transfection in K562 cells.
(B, C, D and E) Co-immunoprecipitation experiments examining the interactions between MLL complex components. Nuclear extracts from control or SON siRNA transfected K562 cells were subjected to immunoprecipitation with MLL-N (B), WDR5 (C), LEGF (D) or SET1A (E) antibodies. The immunoprecipitates were analyzed by Western blot with indicated antibodies.
(F) Interaction of SON with menin. K562 nuclear extracts were immunoprecipitated with control IgG or SON antibody (SON-N Ab) and several components of the MLL complex were examined by Western blot.
(G) Verification of the SON-menin interaction. HEK 293 cells transfected with HA-SON, Flag-menin or pcDNA3-control as indicated were used for co-immunoprecipitation with HA antibody followed by Western blotting with HA or Flag antibodies.
(H) Immunoprecipitation experiment in K562 cells transfected with V5-tagged SON indicates that SON outcompetes MLL (MLL-N) for menin interaction in a dose-dependent manner. For plasmid transfection, two different amounts of SON-V5 construct, 5 µg (+) or 10 µg (++), were used. See also Figure S4.