Figure 8.
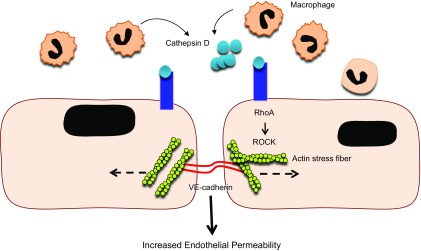
A schematic diagram highlights the cause and effect of CD in altered vascular permeability in retinal capillaries in diabetes. In diabetes, there is increased Mono trafficking in retinal tissues, and Monos are further differentiated into Mϕs that secrete CD. The CD then binds to the CIMPR on the EC surface, activating the Rho/ROCK pathway, which results in a significant increase in actin stress fiber density and thickness. This leads to EC separation and increased endothelial permeability, and alteration of the BRB.