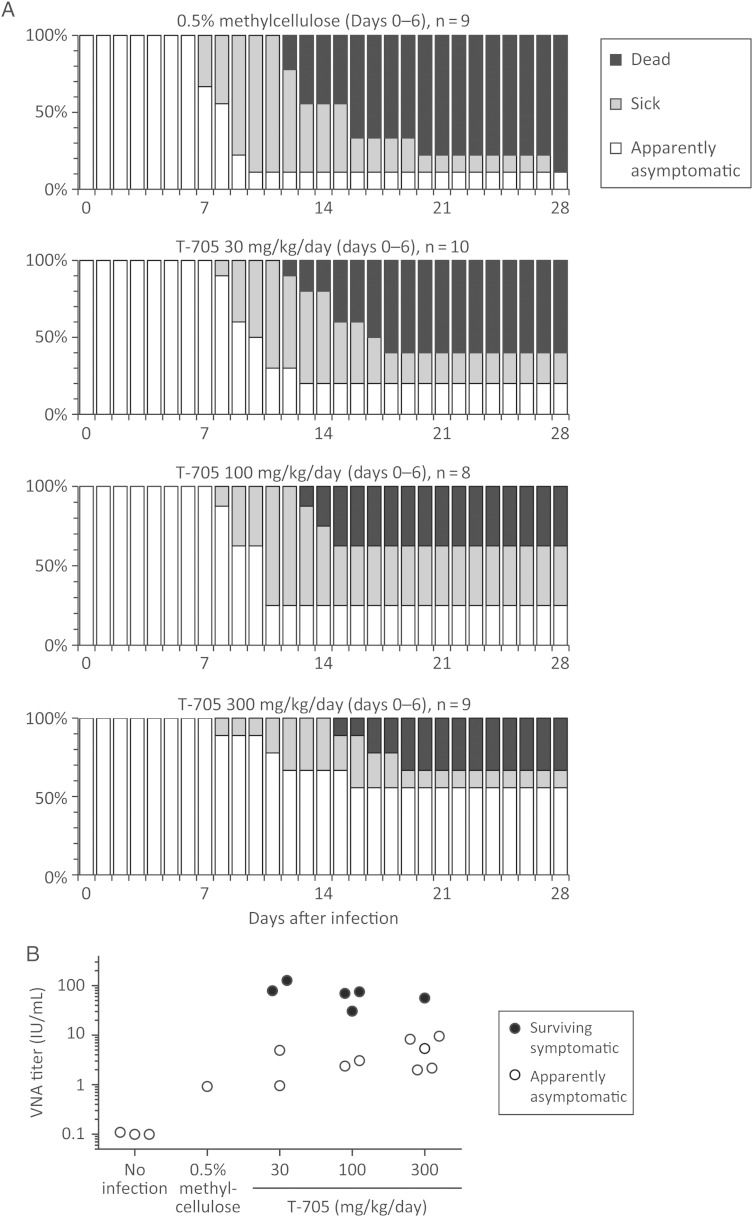
Figure 3.
Efficacy of postexposure T-705 administration for 7 days in mice infected with 1088. A, Mice were intramuscularly inoculated with 1088 and orally administered T-705 (30, 100, or 300 mg/kg/day) or 0.5% methylcellulose (as a control) daily for 7 days (days 0–6) beginning 1 hour after inoculation. Mice were monitored for 28 days. “Sick” indicates that mice showed significant body weight loss or neurological signs. Surviving sick mice had begun to gain body weight but with sequelae, such as limb paralysis. For the survival curves, a significant difference was observed between the control and T-705 (300 mg/kg/day) groups (P < .01, by the log-rank test) but not between the control and T-705 (30 or 100 mg/kg/day) groups (P ≥ .05, by the log-rank test). B, The VNA titers in sera of surviving mice. Sera were collected at 28 days after inoculation, and the titers were determined by a rapid fluorescent focus inhibition test.